The OpenSea business model has scalable capabilities centered around allowing users to purchase, sell, and trade non-fungible tokens via its website. They make money through service fees generated whenever a digital asset is sold on their website. Since its launch, OpenSea has raised more than $421 million through NFT sales.
Contents
A brief history of OpenSea
OpenSea was founded in 2017 by Devin Finzer and Alex Atallah. The platform created a revenue source for game developers like CryptoKitties looking for ways to generate profit from their game characters.
Devin together with Alex drafted some rough business drafts and applied for a grant from YCombinator, from which they got their initial funding of $120,000. At its launch, their project focused on the concept of using blockchain technology to share Wi-Fi bandwidth.
In early 2018, they released OpenSea, and, by March of the same year, they had already sold digital collectibles worth more than $500,000.
By the end of 2019, OpenSea became the undisputed leader among NFT marketplaces, and this was achieved thanks to their acquisition of business competitor Atomic Bazaar and the introduction of more features, like the sale of digital assets in bundles, which also helped to offset Ethereum gas fees. The investments by high crypto investors, such as 1confirmation, Founders Fund, and Blockchain Capital, who injected more than $2 million into the business, also helped to boost the business.
Who Owns OpenSea
As a very recently founded company, OpenSea is, as presumable, owned by its founders: While Alex Atallah remains a Co-Founder, Devin Finzer holds the position as the CEO. Furthermore, Nadav Hollander is the CTO, and Brian Roberts is in charge of the CFO position.
OpenSea’s Mission Statement
“To build an open digital economy”
How OpenSea makes money
OpenSea offers the infrastructure of its platform free of charge, however, the business model dictates that they take a percentage of the transaction fee as a service fee. Their fee structure matches the likes of other NFT marketplaces like Rarible.
To encourage NFT buyers and sellers to use the platform, OpenSea covers all Ethereum gas fees for all transactions on the platform.
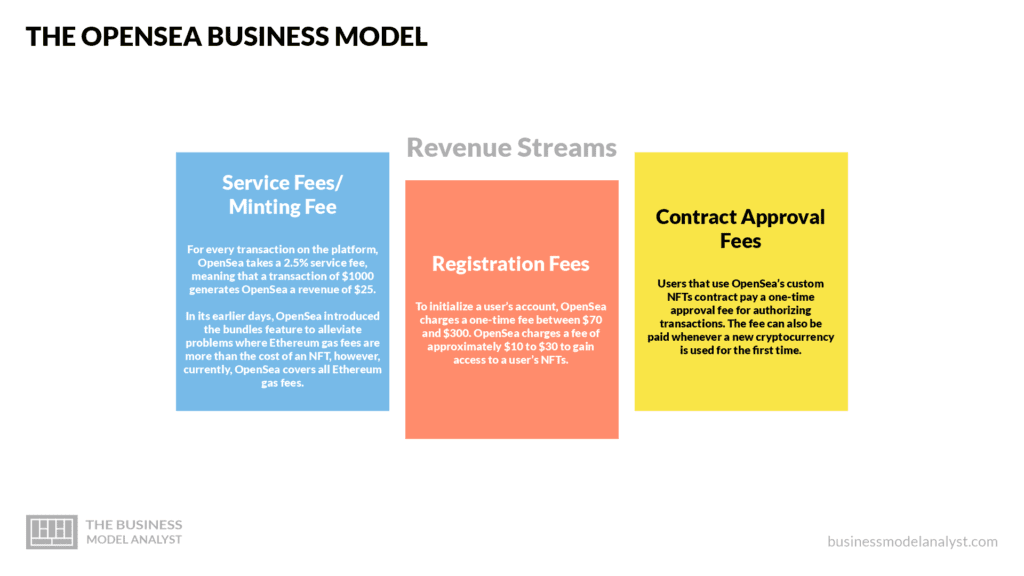
Service Fees/Minting Fee
For every transaction on the platform, OpenSea takes a 2.5% service fee, meaning that a transaction of $1000 generates OpenSea a revenue of $25.
In its earlier days, OpenSea introduced the bundles feature to alleviate problems where Ethereum gas fees are more than the cost of an NFT, however, currently, OpenSea covers all Ethereum gas fees.
Registration Fees
To initialize a user’s account, OpenSea charges a one-time fee between $70 and $300. OpenSea charges a fee of approximately $10 to $30 to gain access to a user’s NFTs.
Contract Approval Fees
Users that use OpenSea’s custom NFTs contract pay a one-time approval fee for authorizing transactions. The fee can also be paid whenever a new cryptocurrency is used for the first time.
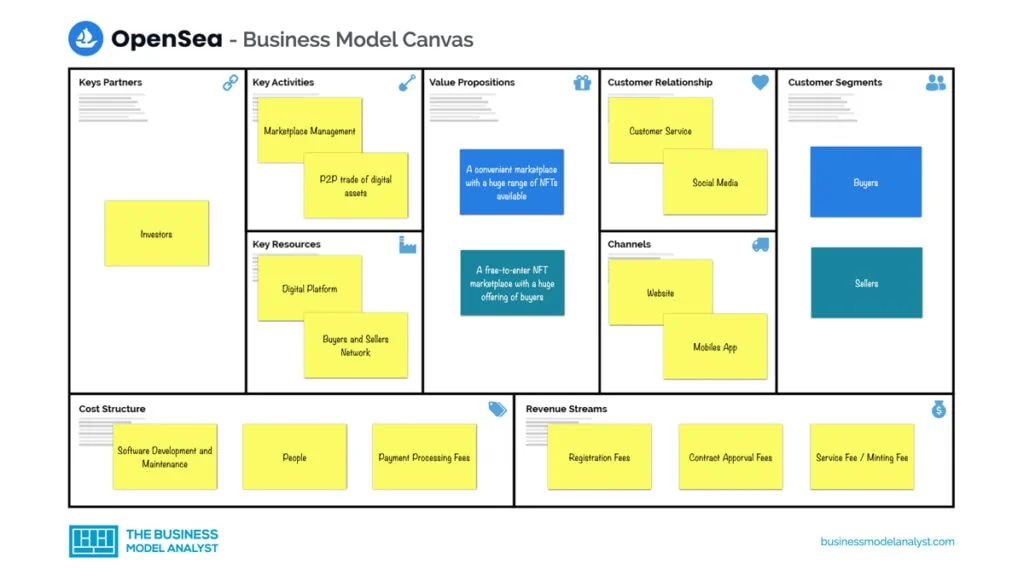
OpenSea’s Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the OpenSea Business Model Canvas below:
OpenSea’s Customer Segments
OpenSea’s customer segments consist of:
- Buyers: People who buy NFTs from others, in the case of a popular NFT, buyers engage in auctions to outbid others;
- Sellers: They design, advertise, and sell NFTs either as single assets or as a collection (bundle).
OpenSea’s Value Propositions
OpenSea’s value propositions consist of:
- Buyers: A convenient marketplace with a huge range of NFTs available. Ethereum gas fees have been covered by the platform;
- Sellers: A free-to-enter NFT marketplace with a huge offering of buyers. Service fees are only a small fraction of the total NFT cost. With the platform covering the gas fees, there’s more profit to be made.
OpenSea’s Channels
OpenSea’s channels consist of:
- Website
- App for Android and iOS
OpenSea’s Customer Relationships
OpenSea’s customer relationships consist of:
- Customer Service
- Social Media
OpenSea’s Revenue Streams
OpenSea’s revenue streams consist of:
- Service Fee/Minting Fee
- Registration Fees
- Contract Approval Fees
OpenSea’s Key Resources
OpenSea’s key resources consist of:
- App and Web Services
- Active Sellers & Buyers
- Digital Assets
OpenSea’s Key Activities
OpenSea’s key activities consist of:
- Payment Processing
- Marketplace Management
- Peer-to-Peer trade of digital assets
OpenSea’s Key Partners
OpenSea’s key partners consist of:
- Investors
- Buyers
- Sellers
OpenSea’s Cost Structure
OpenSea’s cost structure consists of:
- Payment Processing Fees
- Salaries
- Website Maintenance
OpenSea’s Competitors
- Rarible: Based in Moscow and founded in 2020 by Alex Salnikov and Alexei Falin. Unlike OpenSea, Rarible charges both buyers and sellers a 2.5% service fee, however, the seller can decide to cover the whole 5%. Rarible issued its own governance token (RARI) in July 2020;
- Mintable: Founded in 2018 by Mark Cuban-backed Mark Burks, Mintable is a digital asset marketplace just like OpenSea, the platform also offers NFT minting services. However, it differentiates itself by making the trade of digital assets possible with fiat currency;
- SuperRare: Founded in 2017 by John Crain, Charles Crain, and Johnathan Perkins, they are also the founder of Pixura, the company building the crypto collectible technology in use by SuperRare. The platform allows NFT creators to gain additional profit whenever their digital assets are resold. SurperRare takes a 15% cut of the first sale, leaving the creator with 85% and an additional 3% for every resale;
- KnownOrigin: Founded by David Moore, Andy Gray, and James Morgan in 2018, KnownOrigin has generated more than $1.3 million in sales. They have worked with brands like Netflix, Adobe, and Adidas, and just like SuperRare, they have developed secondary sale systems;
- Coinbase NFT: One of OpenSea’s biggest rivals, Coinbase already has more than 1.1 million users signed up on its NFT waitlist, which trumps OpenSea’s total active user base. Coinbase NFT has already partnered with collections like World of Women, DeadFellaz, and Lazy Lions;
- FTX NFTs: Unlike OpenSea, FTX NFTs do not use P2P systems, the platform is centralized and custodial, and, as a result, users’ data is stored on its network. Full anonymity isn’t offered by the platform.
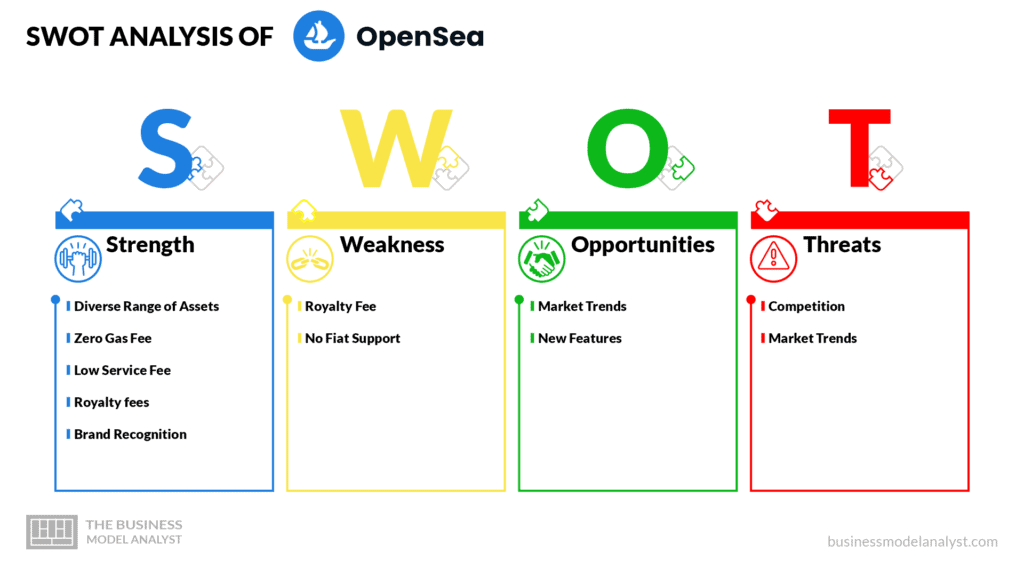
OpenSea’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of OpenSea:
OpenSea’s Strengths
- Diverse Range of Assets: OpenSea’s position as the first NFT marketplace and its acquisition of competitors have allowed them to obtain and offer a large and diverse range of digital assets;
- Zero Gas Fee: Like most of its competitors, OpenSea has waived Ethereum gas fees for its users in a bid to make the platform much more attractive;
- Low Service Fee: OpenSea unlike its competitors maintains a service fee or minting fee charge of 2.5%, which has given them the needed edge to remain the undisputed marketplace for digital assets;
- Royalty fees: Creators on OpenSea can attach a 10% royalty on their asset for every resale it accumulates;
- Brand Recognition: Their first marketplace status has made the platform a popular, trusted space for digital assets trade.
OpenSea’s Weaknesses
- Royalty Fee: The ability of original creators to attach royalty fees of up to 10% to their assets reduces the profit of resellers;
- No Fiat Support: Unlike competitors like Mintable and SuperRare, OpenSea doesn’t support the trade of digital assets with fiat currencies.
OpenSea’s Opportunities
- Market Trends: With the recent growth in NFT and Metaverse stocks and popularity, and with more games incorporating NFTs into their gameplay, the market demand for an efficient asset marketplace with a low entry barrier is on the rise;
- New Features: Features like Collection Manager with zero gas fees, and the introduction of new features, will set it aside from its competitors while ensuring that it retains its number one title.
OpenSea’s Threats
- Competition: With the establishment of new marketplaces, a new wave of rivalry and competition is set to begin in the digital assets’ ecosystem;
- Market Trends: Just as the popularity of digital assets has grown, there is a chance that it will eventually fall, leading to a decrease in OpenSea’s revenue generation. This is already happening with the current reduction in assets trade in comparison to 2021.
Conclusion
OpenSea is a marketplace for trading digital assets, and the OpenSea business model is based on minimal transaction fees. As the platform gets more popular, more and more transactions are expected to happen on OpenSea, which will result in more revenue from transaction fees.
Their value proposition for users is really simple: They want to provide a safe and reliable way for users to buy and sell the digital assets they want, so they don’t have to face the risk of losing thousands of dollars on a scam. Business-wise, that means dedicating a lot of their resources to trust and transparency, and this has continued to increase users’ trust in the platform, resulting in revenue increase.

