In short words, the low cost business model is based on a strategy by which the business offers low prices in order to instigate demand thus, gaining market share. This business model can be adopted by virtually any company, but it is usually indicated in cases when there is no (or little) competitive advantage or when it is easier to achieve scale with production volumes, so they apply the strategy of cost advantage.
Contents
Low Cost Business Model Canvas
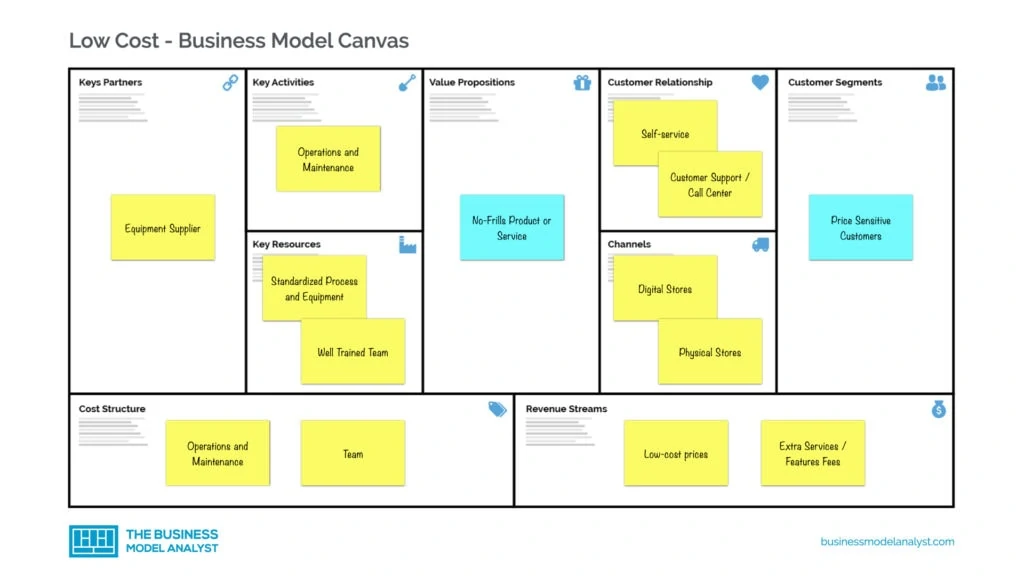
- Low-Cost Customer Segments: Price-sensitive customers are the main target of low-cost businesses, but you can say that this is pretty much a mass-market as well.
- Low-Cost Value Propositions: Low-cost businesses offer no-frills products or services for which the non-essential features have been removed to keep the price low.
- Low-Cost Channels: Digital stores like companies own e-commerce websites and aggregators. Physical stores at airports or high-traffic areas can also be part of the channel strategy.
- Low-Cost Customer Relationship: Usually self-service to avoid high human-resources costs. Customer support, especially if they can be outsourced for low-cost call centers.
- Low-Cost Revenue Streams: Low-cost prices attract customers, but the extra services for non-essential services or product features are what increase profit margins.
- Low-Cost Key Resources: The most important asset is having standardized processes and equipment in place. The operational cost must be minimum therefore optimized.
- Low-Cost Key Activities: Since the low price is responsible for attracting customers, operating the business to deliver the value with a low-cost structure is key.
- Low-Cost Key Partners: A good partnership with suppliers, especially equipment suppliers can make a big difference.
- Low-Cost Cost Structure: Operations and human resources are the heaviest cost in this model.
What is cost advantage?
Simply put, a business may employ the cost advantage when it is able to manufacture some product or provide some service at a lower cost than its competitors. They can apply this advantage in two ways:
- By lowing their prices below the competition, thus attracting more customers, and gaining market share. The low margins will be, then, compensated by higher sales volumes.
- By pricing their products equally as their competition, but having a cheaper cost structure, thus making more profit.
In order to develop a cheap cost structure, these companies benefit from:
- Low-cost raw materials,
- Sustainable processes, technologies, and operations,
- Efficient distribution,
- Low-cost sales strategy,
- Outsourced services,
- Lean manufacturing strategies.
No matter if your customers are regular folks or millionaires, people will always compare prices, and enjoy low prices and discounts. So, it is a useful strategy to increase traffic towards your business. Anyway, there are some challenges and benefits regarding the low cost business model.
Advantages of low cost business model
Bigger profit
When you develop a lean cost structure, you can have greater margins than other companies will usually achieve. This way, you are offering a strong value proposition to your customers – the same product/service at a lower price – and assuring a bigger profit
Improved market share
As said above, customers often consider acquiring a product/service at a lower price, especially when they see the same value as the competitors. The same value proposition at a lower cost will be probably their first choice. Over time, this choice will lead to more businesses, enhancing a greater market share.
Sustainable business
Whenever you have a lean cost structure, you are reducing the risks and threats that your business may face. That turns your company into a more sustainable and secure business. Mainly because if some crisis happens, that causes a price war, your company is already prepared for the circumstances.
Reinvested capital
Over time, the bigger margins may provide a nice capital and resources reserve. And this reserve can be used for many different purposes, reinvesting the profits into the company and fomenting growth or expansion.
Reduced competition
When your company is able to offer a low-cost product or service, it forces the competitors to struggle to reach the same price or lower. But, for an already structured business, it is not usually easy to transform itself to achieve cost leadership. Sometimes, the necessary alterations may make it impossible for the competitor to survive, especially new entrants.
Increased sales
As mentioned above, many times, cost leadership will attract traffic to your business. This will increase your sales. Especially at the beginning of the venture, that is very helpful, in order to pay for the early investments any company needs to do to start running.
Close relationships
To cut costs, one of the most efficient strategies is to keep close communication with the audience, to discover their needs and expectations, avoiding unnecessary and unsuccessful investments. This will also provide closes relationships with suppliers, because the company is able to provide information, thus ensuring the best price and material, and creating a long-term trustful relationship.
Disadvantages of low cost business model
Price War
The competitors may indeed lower their prices to beat yours. Then, you may experiment with a dose of your own medicine: you may need to battle to sell the cheapest and, once you reach your lowest price, you might lose profit. The solution can be to let your audience understand that you have a low price, not necessarily the lowest one.
Poor supplier relationships
As mentioned before, this strategy may enhance your relationship with your suppliers and vendors. But, on the other hand, if you struggle so much to reach your bottom price, making it hard for them to keep up with prices and deliveries, they may give up on you or hand you poor materials to maintain the price.
Low-profit margins
If you can’t handle a price war, crisis, or even negotiations with your suppliers, that may end up in a not so lean cost structure, which can result in low-profit margins. Besides the low income, you will have little capital to reinvest in your business.
Poor quality perception
Once you choose to offer a low price, it is often common that your audience perceives the low price as low quality. This way, you may find it hard to introduce new products or services, especially the ones that require a higher price due to the quality. Your customers may not believe you can offer a higher-quality product/service.
Harmful financial cuts
In order to maintain a low cost business model, you may need to cut some costs to keep up the budget, and these cuts sometimes can actually harm your operations or your value proposition, making the service poor or the operations slow, just to mention some.
Reduced innovation
Usually, R&D will be perceived as expensive in a low cost business model. This may compromise the chances of making innovative products reach the market. Little capital means little possibility for innovations since the business can’t risk investing in new – and possibly risky – ideas.
A large volume of sales required
Cost leadership depends closely on a large volume of sales to keep up its profitability. So, this strategy is usually employed by big brands, such as Costco or Walmart. Local businesses are hardly able to apply that.
The benefits and challenges presented to prove that the low cost business model can be indeed used to create a unique competitive advantage – but the strategy may not be adequate to any kind of business, since it reduces the chance for the company to adapt to any new circumstances.

