Is Uber profitable? The short answer: Uber is not currently profitable. The long answer is a bit more complicated.
Uber operates on a simple yet effective business model. First, Uber recruits drivers to sign up with the platform and provide rides to passengers. Riders can then request a ride through the Uber app, and the nearest available driver is sent to pick them up. The fare is calculated based on the distance traveled and the time taken, and the payment is taken automatically from the passenger’s linked payment account. Uber then takes a commission from the fare, which is typically around 25%. Once all the fees have been collected, the remainder of the fare is paid to the driver.
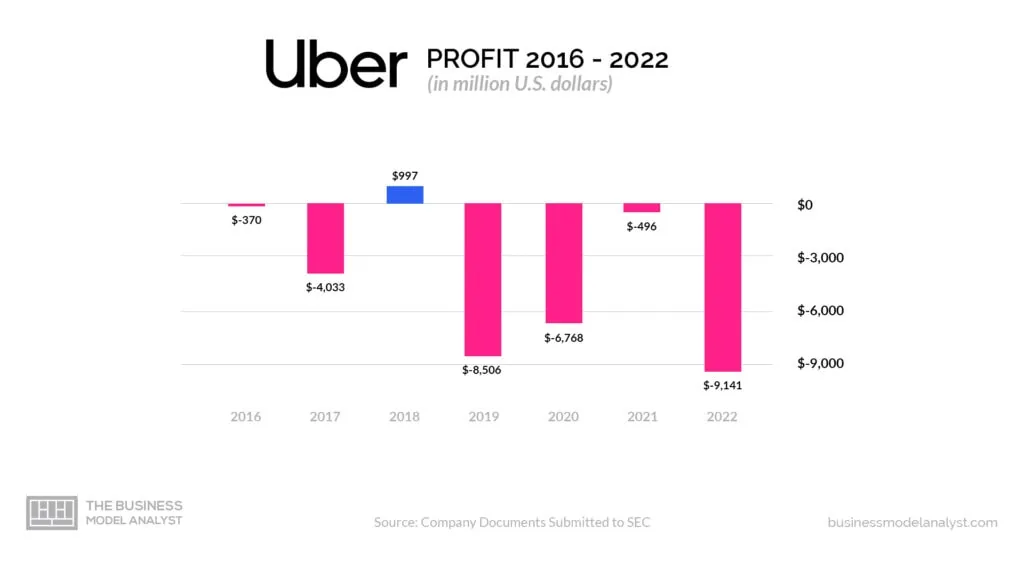
Despite its popularity, Uber has been unable to turn a profit on a net basis. In 2022, Uber reported a profit on an adjusted EBITDA basis, meaning it had generated positive earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. However, the company still lost a large amount of money.
While Uber has seen tremendous growth over the past decade, the company has yet to make a profit. However, this does not mean that Uber is not generating revenue.
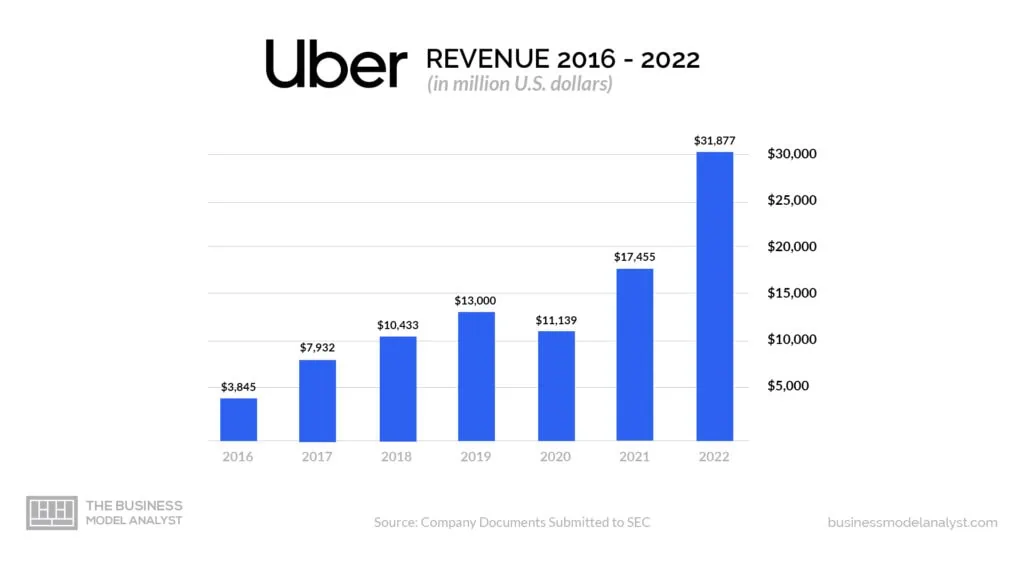
In fact, the company reported over $11 billion in revenue in 2020 and went on to reach over $17 billion in 2021. While Uber has yet to break even, its enormous revenue indicates that the company is well on its way to profitability.
Contents
Timeline of Uber’s financial growth and funding
Uber’s meteoric financial growth and funding have been something to behold. Over the past decade, Uber has gone through numerous rounds of funding and multiple investments, resulting in its explosive financial growth. This timeline highlights the major milestones of Uber’s financial growth and funding throughout its history.
- 2011: Uber raised over $11 million in its first round of venture capital funding;
- 2011: In its Series B round of funding, Uber raised an additional $37 million, and continued to expand to more cities around the world; it would go on to launch UberX the following year;
- 2013: Uber raised $363 million in its first round of late-stage financing, bringing its total funding to over $400 million;
- 2014: Uber raised an additional $1.4 billion in its latest round of funding, bringing its total funding to just under $2 billion;
- 2017: Uber raised $7.7 billion in its Secondary Market funding, with a pre-money valuation of $40.3 billion;
- 2019: Uber went public on the New York Stock Exchange and raised an additional $8.1 billion in its initial public offering.
In total, from 2011 to 2020 (a post-IPO debt round), after 32 rounds of funding, Uber raised $25.2 billion.
Financial Performance of Uber
Overview of revenues, expenses, and profits
Uber is one of the most successful ride-sharing companies in the United States. It has a presence in more than 10,000 cities worldwide. According to CNBC, Uber generated $12.7 billion in gross bookings in the third quarter of 2018. On an adjusted pro-forma basis, it recorded a net loss of $768 million in the fourth quarter of 2018.
Uber’s revenue is derived from the fees it charges users for its services. This includes booking fees, surge pricing fees, and other fees. Uber also generates revenue through its partnerships with other companies, such as Spotify and delivery services.
Uber’s expenses include operational costs such as driver payments, marketing, and technology expenses. Uber also pays local governments for licenses, taxes, and other fees. In the fourth quarter of 2021, Uber’s net income was $892 million. This was a relatively significant increase from the net income of $540 million reported in the fourth quarter of 2020. However, for the same year, Uber recorded an annual net income of $-0.496 billion.
Analysis of disruptive impact on the traditional taxi industry
Uber has had a disruptive impact on the traditional taxi industry. Uber’s business model relies on technology to match riders with drivers and provide low-cost rides. This has allowed Uber to undercut traditional taxi fares. This has resulted in traditional taxi drivers facing competition from Uber drivers, as well as reduced income.
Uber’s impact on the traditional taxi industry has been both positive and negative. On the positive side, Uber has expanded the ride-sharing market, increased competition, and made it easier for customers to get a ride.
On the negative side, Uber’s lower fares have made it difficult for traditional taxi drivers to compete. This has led to a decrease in the supply of traditional taxi drivers, as well as fewer opportunities for traditional taxi drivers to earn an income.
Uber Business Financials
Uber operates several other businesses, such as food delivery, freight, e-bikes, and scooters. Uber’s businesses have grown significantly in recent years.
Its core ride-sharing business has been its primary source of revenue since its launch in 2009. In Q4 2021, Uber processed $11.3 billion in gross bookings from its ride-sharing operations. This is a significant increase from the $6.7 billion in gross bookings that the company reported in 2020. Uber also reported over $2 billion in revenue from ride-sharing in the fourth quarter of 2021.
Uber’s food delivery business, Uber Eats, has also been a major contributor to the company’s revenues. In Q4 of 2021, Uber reported $13.4 billion in gross bookings from Uber Eats. This is up from just $10.05 billion in gross bookings reported in the fourth quarter of 2020. Uber also reported over $2.4 billion in revenue from their non-freight delivery service in the 4th quarter of 2020.
Uber’s other businesses, including Uber Freight, Jump Bikes and Scooters, and Uber Health, are also generating significant amounts of revenue. In the Q4 of 2021, Uber reported $1.08 billion in gross bookings from its freight business. This is up from $313 million in gross bookings reported in the fourth quarter of 2020. This marked a 245% growth in revenue.
In total, Uber generated $17.455 billion in revenue in 2021. This is an increase from the $11.139 billion in revenue that the company reported in 2020. However, Uber also reported a net income of -$6.7 billion in 2020. This is up from the $-8.506 billion in net income that the company reported in 2019. These figures suggest that Uber is still struggling with profitability. Although the company is still growing, others worry that its rapid growth is unsustainable and that it will not be able to attain profitability in the long run.
Potential for Profitability
Uber has the potential to be an incredibly profitable company. The company operates in more than 10,000 cities around the world, providing its services to millions of customers. This means that Uber has a large customer base to tap into, and its market share continues to grow in many cities. With a large customer base, Uber can generate significant revenues through fares and other services such as Uber Eats. Also, Uber has a number of partnerships with other companies, such as Starbucks, that can increase its profitability.
Uber also benefits from its low overhead costs, as the company does not own or maintain a fleet of cars. Instead, Uber relies on independent drivers, allowing it to keep its costs low and maximize its profits. Uber’s efficient business model allows it to quickly scale up its operations, which helps increase its profits.
Challenges that Uber faces as a business
Despite its potential for profitability, Uber has faced some significant challenges as a business. For one, the company has faced multiple legal issues, including labor disputes, class-action lawsuits, and regulatory issues. Uber has struggled to hold onto market share in several areas due to stiff competition in the ride-sharing industry. Customers who feel that Uber’s fare structure is excessively high have also questioned the company’s pricing strategy. Additionally, regulators have previously questioned its data security and privacy policies, which have drawn criticism.
Strategies to profitability
To achieve profitability, Uber has to employ several different strategies. First, the company should work to improve its legal compliance and address any labor disputes or class-action lawsuits. It can also focus on improving customer satisfaction. This can be done by providing incentives for customers to take more rides, such as discounted fares or loyalty programs. In addition, Uber should focus on improving its services by adding more features or expanding into new areas.
Uber can also focus on reducing its costs. This can be done by improving its technology, such as by using more efficient driver selection algorithms or by expanding its driver pool. The company can also explore partnerships with other companies that can help it reduce costs, such as offering discounts for rides or offering incentives to customers. It could also look to increase its marketing efforts to attract more customers, as a way to increase its revenues.
Conclusion
It is clear that Uber is not currently profitable. Despite its efforts to reduce costs and increase revenue, the company has yet to find a way to achieve sustainable profitability. However, there is potential for profitability given Uber’s increasing number of users and market share, as well as its widespread recognition as an innovative force in the ride-sharing industry.
To become a profitable enterprise, Uber must continue to adjust its pricing, reduce overhead costs, and look for innovative ways to increase revenue. With significant support from investors, Uber has the resources to continue optimizing its business model to achieve sustainability.
Ultimately, Uber’s success will come down to its ability to continue innovating and meeting the needs of its diverse customer base.


