Is Google profitable? Quarter three of 2021 was one of the most profitable moments for Google. The company recorded $65.1 billion in revenue and $18.9 billion in profit, marking its fifth straight quarter of immense profits. However, Alphabet, Google’s parent company, reported that the company’s profits slipped last summer, despite generating more revenue. In the 2022 third quarter, Google generated $69 billion in revenue and $13.9 billion in profit.
Most of the company’s businesses have recorded growth year over year, with advertising generating $54.4 billion, an increase from $53.1 the previous quarter. Google Cloud generated $6.9 billion in 2022 from $4.9 in quarter three of the last year. Still, Google’s losses from its cloud division rose from $644 million to $699 million. Speaking during the company’s earnings call, Sundar Pichai, the CEO, mentioned that Google recently experienced its “highest selling week ever for Pixel” after introducing the Pixel 7 and 7 Pro and its Pixel Watch.
Google has recently ventured into wearable technology, driverless vehicles, renewable energy, and mobile operating systems. The more the company diversifies its interests, the more its revenue rises. During the 2022 first quarter, the company generated $67.3 billion in revenue, hitting $69.69 billion during the second quarter, a $62 billion increase from the same period the previous year.
Today, Google is the leading source of knowledge for internet users. Before the company went public in 2004, searching for information was a challenging activity. The company has revolutionized how people access information.
Contents
Timeline of Google Financial Growth and Funding
1998-2008: Google was officially founded in September 1998. However, its story starts in 1995 when two students met at Stanford University, forming a partnership to build a search engine called Backrub. They would later name it Google. Soon, Google caught the attention of both the academic community and Silicon Valley investors. In 1998, Sergey and Larry received $100,000 from Andy Bechtolsheim, Sun co-founder, and Google Inc. was birthed. With this money, the team hired its first office, a garage, in suburban Menlo Park, California.
The company received other angel investors, including Jeff Bezos, the Amazon founder, David Cheriton, a computer science professor at Stanford University, and Ram Shriram, an entrepreneur. In total, the company raised approximately $1,000,000. Google Friends was launched the same year to inform fans about the company. In 1999, Google moved offices to Palo Alto, California, home to various well-known Silicon Valley start-ups.
A $25 million round of funding was also announced the same year. The company started selling advertisements affiliated with search keywords in 2000. In the same year, Google became Yahoo’s default search engine provider. The company also won a people’s voice award for technical achievement and a Webby Award for the best technical achievement in 2000. Google’s billion-page index was launched in June 2000. By then, 18 million queries were logged on the platform daily, making it the largest search engine globally. In 2001 Google hit the 100 million search mark per day. Besides acquiring all of Deja.com’s assets, the company launched Google PhoneBook. The company’s list of customers continued to grow in 2001.
By mid that year, the company powered 130 destination and portal sites in 30 countries, while advertising programs attracted over 350 premium Sponsorship advertisers. The company acquired a patent for its PageRank technique in the same year. In 2003 Google leased an office complex from Silicon Graphics, which they later bought for $319 million. Google later signed a multi-year agreement with AOL to provide results to the company’s 34 million members and numerous AOL.com visitors.
Page and Brin approached Yahoo with a $3 billion offer, but the CEO refused. The company introduced Google Labs the same year. In 2003 Google acquired Applied Semantics, the AdSense makers, for $102 million. By 2004, Google had over 800 employees. The company announced its IPO the same year, raising $1.66 billion. The company would pay another $102 million in 2006 to acquire dMarc Broadcasting, a web advertisement business. Google made one of its most significant acquisitions in 2007 by buying DoubleClick, an online advertising company, for $3.1 billion.
2007-2017: In response to the massive mobile applications growth, Google acquired Admob, a mobile advertising network, for $750 million in 2007. Google’s shares first hit $700 on October 31, 2007. Individual investors triggered the increase in stock price. The same year, Fortune rankings showed Google was the leading company to work for. In 2008, groups of publishers and authors sued Google for availing their copyrighted books online. Google later agreed to pay the groups $125 million.
The company also offered the publishers and authors 63% of advertising revenue from page views of their content on Google’s website. In exchange, the publishers and authors would allow internet users to read sections of their work online. Google Chrome was birthed in 2008, becoming one of the most popular browsers globally. Google Voice was launched in 2009. Google acquired Motorola Mobility for $12.5 billion in 2012, making it its most significant acquisition. In June 2013, Google bought Waze in a $966 million deal.
As of September 2013, Google had 70 offices in over 40 countries. Google’s consolidated revenue for the 2013 third quarter was $14.89 billion, a 12% rise from the previous quarter. $10.8 billion of this total was from Google’s Internet business. In 2014, Google announced the acquisition of DeepMind Technologies, reportedly for $400 million. Sundar Pichai replaced Larry Page as Google’s CEO in 2015. The same year, the company underwent a division restructuring process under Alphabet.
In 2016 Google announced discontinuing the Picasa web albums service and Picasa desktop application. It also launched an online search firm. By then, it offered over 50 internet products and services for tablet computers and mobile phones.
With its massive size and diverse product portfolio, Google became one of the most influential companies in the high-technology industry. In 2016, Alphabet generated almost all of its revenue from Google advertising. In 2017 Google introduced Google News, a content aggregation service that would transform the publication and distribution of digital media on the internet. Google and Alphabet, its parent company, has an $800 billion market cap.
2019-2022: Google announced its entry into the video game industry, launching Google Stadia, a cloud gaming platform. In 2020 an antitrust lawsuit was filed against the company, claiming the company had gone against a monopoly position in the search advertising and search markets.
Following the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020, Google announced a raft of cost-cutting measures, which included cutting down hiring for the rest of 2020. Reports indicate that Google paid $20 million for Ubisoft ports on Google Stadia. The company invested colossal amounts of money in getting major publishers like Take-Two and Ubisoft to bring some of the most significant games to Stadia.
Google made its largest acquisition in 2022 when it bought Alter, a digital avatar company, for $100 million. Earlier that year, the company had acquired Mandiant, a cybersecurity firm, for $5.4 billion.
Google Financial Performance: Revenues, Expenses, and Profit
When Google’s quarter three 2022 earnings were recently announced, there was a 27% profit decline compared to the previous year. While revenue increased by 6% year-over-year to hit $69.1 billion, it was a massive growth drop from the same period the previous year, which recorded a 41% increase.
Profits were $13.9 billion, a drop from $18.9 billion in the same period the previous year. The drop was attributed to reduced spending from the crypto, mortgage, loan, and insurance subgroups, with customers cutting ad budgets due to inflation and economic instability. According to Alphabet, Google’s parent company, the most considerable losses were from Google Cloud and Other Bets.
The latter lost $1.6 billion, an increase from a $1.29 loss experienced the previous year. Google Cloud lost $699 million during this quarter, an increase from $644 million in quarter three of 2021.
Google Revenue
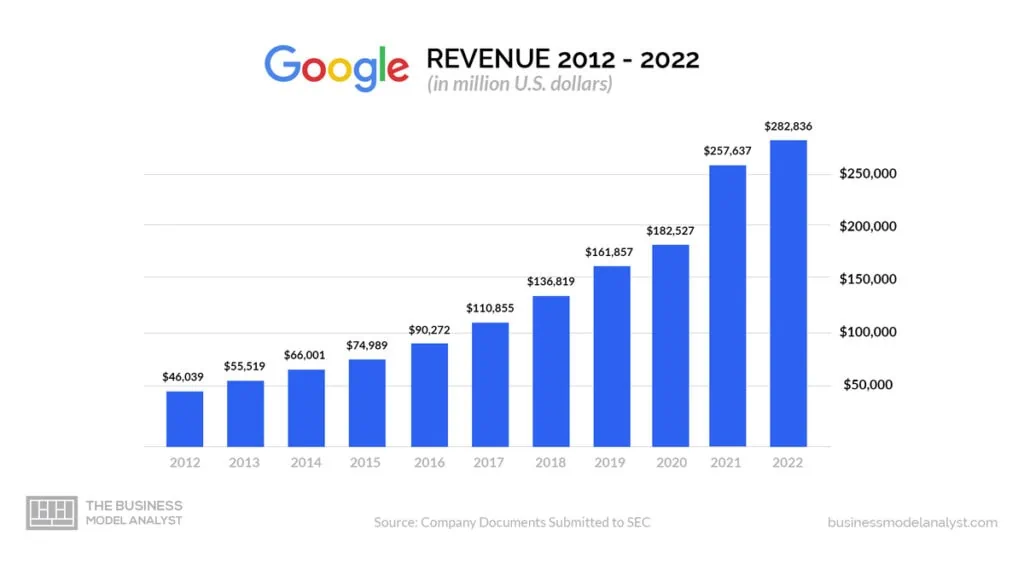
Recent data suggests that Google earned the most revenue from ads in 2021. Out of its $256.74 billion in revenue, $148.95 was from search ads, including ads of Google Play, Google Maps, Gmail, and on the platform’s search engine results page. Ads represented 58% of its overall revenue globally in 2022. Google Network ads were the company’s second-largest revenue source, generating $31.7 billion, representing 12.3% of the total revenue.
This amount was inclusive of ads appearing on Google’s partner websites. YouTube’s ads were the third-largest income source for Google at $28.85, representing 11.2% of Google’s overall revenue. Content generated $28.03 billion in revenue, representing 10.9% of the overall revenue. Revenue from Google Cloud was $19.21, representing approximately 7.5% of Google’s 2021 revenue.
Google Expenses
Google’s lobbying expenses for the 2022 first quarter were $2.96 million, which increased from the previous year’s $2.11 million. According to Alphabet, Google’s parent company’s research and development expenses for December 31, 2022, quarter were $10.267 billion, marking a 17.9% rise year-over-year. The exact costs for the year were $39.5 billion, a 25.15% rise year-over-year.
In 2021, the total research and development expenses were $31.562 billion, a 14.47% rise from 2020. SG&A expenses for 2022 were $42.29 billion, a 16.11% rise year-over-year, while in 2021, the company spent $36.422 billion on the exact costs, a 25.6% increase from the previous year.
Google Profit
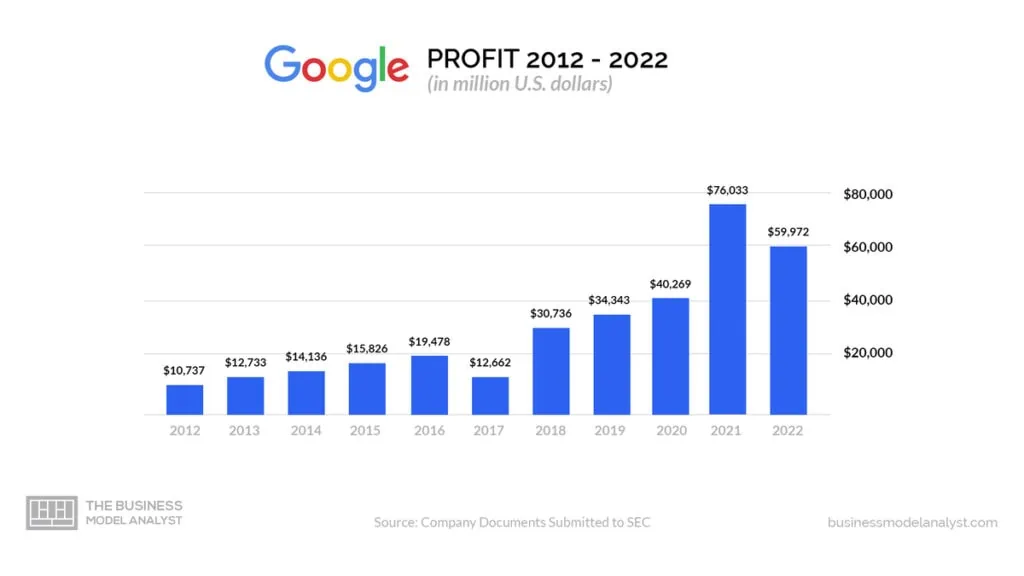
In 2022, Google generated nearly $60 billion in net profits, a drop compared to 2021’s $76 billion. Reports from Alphabet (GooG) indicated that the company’s gross earnings for 2022 were $156.63 billion, a 6.77% increase year-on-year. In 2021, the gross profit was $146.69 billion, a 50.1 rise from the previous year, while the company recorded $97.795 billion, an 8.715 rise from the prior year.
Potential for Profitability
Undoubtedly, Google is one of the largest technology companies in the industry. Still, it can do much more to boost its profitability. Besides the search engine and Android, Google can leverage its Cloud services, such as Google Photos and Google Drive, to generate more revenue.
Customers utilize these services to store their data. Previously, the company offered limited storage free of charge. With the demand for cloud storage rising, the company can provide extra space for premium prices. The company has already adopted this strategy. The wearable industry is overgrowing, and Google can earn attractive revenue. The company is trying to penetrate the industry currently dominated by Apple.
The company should strive to ensure Wear OS is more available and convenient to ensure more people use it. In 2021, Google’s Wear OS had a 17% market share, compared to Apple’s watchOS, which held nearly 22% market share.
When Google Glass was launched, the world wasn’t prepared for it, meaning it didn’t attract the proper attention. People were amid a technological bombardment, and many didn’t like it. With more people becoming techno savvy, an advanced Google Glass would make more sense.
Google must also venture into non-ad revenues to remain profitable. Current indications suggest the company is adapting, as is evident from using commercial transactions through its many sites like Google Maps and Google Books. Currently, a huge chunk of Google’s profits comes from advertisements.
The advertising world is volatile and can succumb to competitor ads easily. Google should venture into different avenues to earn revenue and promote commercial transactions via the numerous apps Google owns. Google can venture into artificial intelligence, robotics, and machine learning industries. The company is already eyeing driverless cars and has penetrated the smart home sector by introducing the Google Home speaker. The company also ventured into the health industry after acquiring Fitbit for $2 billion.
Conclusion
The Google multinational company will be around for many years to come. Based on its structure, it will continue collecting user data, providing customized advertisements, and acquiring companies for large sums of money. It will be long before another search company topples the search engine world. While Google is a successful company, some of its products are performing dismally in terms of generating revenue and profits. Some are even making losses, which is not suitable for the company’s reputation. Google should work with stakeholders and experts to determine how to stabilize revenue and profits.


