Is Amazon Profitable? For the year 2022, Amazon recorded a net loss of $2.722 billion on revenue of $513.98 billion, meaning the company was not profitable in 2022. The company’s profit experienced a sharp decline from its record net income of $33 billion in 2021, ending its 6-year streak of profitability. Despite Amazon recording a net income of $11 billion for the 12-month period ending September 30th, 2022, its year-end report showed a dramatic net loss—the biggest in the company’s history.
The remarkable success of Amazon, the global e-commerce giant, despite its net loss in 2022, is widely recognized as one of the great business successes of modern times. Founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos, Amazon has grown exponentially and now controls nearly half of the entire online retail market. As such, it’s a hugely successful business — but how profitable is it? And is it all that profitable?
Contents
Timeline of Amazon’s financial growth and funding
The timeline of Amazon’s financial growth and funding is a long one. Amazon was founded in 1994, and since that time, the company has grown from an online bookstore to become one of the world’s largest e-commerce companies. Over the past two decades, Amazon’s financial history has been dotted with key milestones that have helped shape its incredible growth trajectory.
1994-1995: Founded by Jeff Bezos as an online bookseller and launched with $250,000 in angel investment money. That same year, Amazon raised additional capital from Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers (KPCB) — its first institutional investor — which gave it enough funding to begin building out infrastructure and hiring new employees to support the growing business.
1997: The company conducted its initial public offering (IPO) at $18 per share, raising over $54 million in what proved to be a successful debut on the stock market. This gave the company access to much larger amounts of capital for expansion purposes thereafter. The IPO led the company to a valuation of $438 million.
1999–2000: The company rapidly grew revenue across both domestic and international markets while also expanding into new categories such as music, movies, electronics, apparel, toys/games, health/beauty care items, and home goods — now selling millions of products across multiple categories and geographies.
2002–2004: Continued their rapid expansion during this period by launching new services such as AWS web hosting services; fulfillment centers around the globe; Kindle e-reading device; Prime loyalty program; marketplace store; streaming video service; an app store for Android devices; and a marketplace offering third party sellers’ products alongside their inventory selection, among other innovative offerings. This period saw annual sales jump from $3.9 billion in 2002 to nearly $6.9 billion by 2004.
2007–2012: Launched initiatives such as AmazonFresh grocery delivery service; Cloud Drive cloud storage system for consumers; audiobook platform Audible purchased for nearly $300 million in 2008–09 plus many other strategic acquisitions worldwide since then like Zappos (online shoe retailer). By the end of this period, annual revenue exceeded $61 billion thanks to these initiatives. However, the company reported a net income of -$39 million, a negative record that would only happen again in 2014.
2013 onward: Had tremendous success extending beyond retailing, including ventures investing heavily into the development of technologies like robotics automation systems used within warehouses around countries like China, Japan, UK, etc.; an Echo-connected home assistant product line; drone delivery experimentation, etc.
Amazon kept pushing forward investments in several different industries, which all fueled phenomenal growth, making them profitable every year since 2014. However, in 2022, the company experienced its highest net loss yet, at $2.7 billion. This loss can be attributed to their status as the biggest advertiser in history, among other reasons.
When did Amazon first become profitable?
According to Ycharts and GlobalData, Amazon first became a profitable company in 2003, when it reported an annual net income of $35 million. Its profitability run came to a halt in 2012, when it reported its first loss of the new decade. Two years before that, it had reported an annual net income of $1.152 billion. Its next negative net income would come in 2014 at a loss of $241 million, after which it recovered with a profit of $596 million in 2015. In 2021, it reported its highest net income yet, at $33.35 billion.
Financial Performance of Amazon
The financial performance of Amazon can be split into two broad categories: revenues and expenses. Amazon’s revenues are split into three core categories: North America, International, and AWS (Amazon Web Services). In 2019, Amazon reported total revenues of $280.5 billion, with $170.77 billion from North America, $74.7 billion from international, and $35 billion from AWS. In terms of expenses, Amazon reported total operating expenses of $265.9 billion in 2019. The company’s net income, however, was a more modest $11.6 billion.
Amazon Overview of Revenues, Expenses, and Profits
Amazon’s Revenue
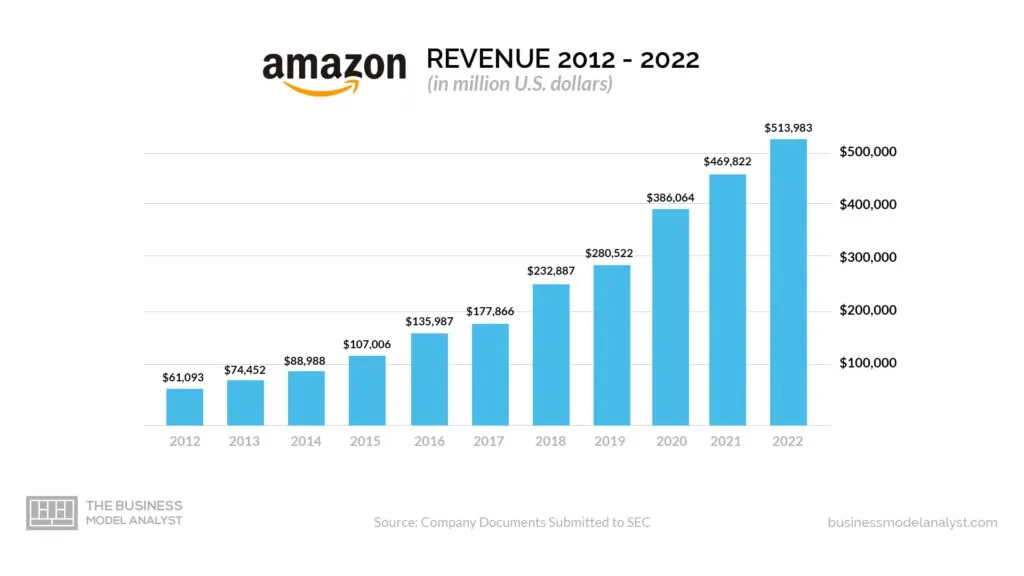
Amazon generates revenues from retail sales, subscription services, web hosting services, and other business activities. For the year 2022, Amazon reported $514 billion in total revenue, which was a 9% increase from 2021. Its biggest source of revenue came from its North American segment, which accounted for 61.4% of total revenue, or $315.9 billion ($279.9 billion in 2021). The International segment represented 22.95% of revenues, or $118 billion ($127.8 billion in 2021), while the other AWS segment contributed just 15.58%, or $80.1 billion ($62 billion in 2021). The company also recorded an operating income of $12.248 billion versus $24.879 billion the year prior.
Amazon’s Expenses
In addition to generating large revenues through various sources, Amazon also incurs massive costs each year to keep its business running smoothly. In 2022, Amazon reported total operating expenses of approximately $501.735 billion ($444 billion in 2021), which included the cost of goods sold (COGS), fulfillment expenses such as shipping and technology, content expenses like software development costs, marketing and promotion expenses including advertising campaigns and promotional offers made to customers, plus general and administrative (G&A) spending on traveling and office needs, among others. That same year, they reported that COGS totaled over $288.831 billion ($272.344 billion in 2021), while fulfillment expenses amounted to around $84.299 billion ($75 billion in 2021). Technology and content expenses stood at $73.213 billion (a 30% increase from 2021), with marketing and promotion costs going up to $42.238 billion (a 29.75% increase from 2021).
Amazon’s Profits
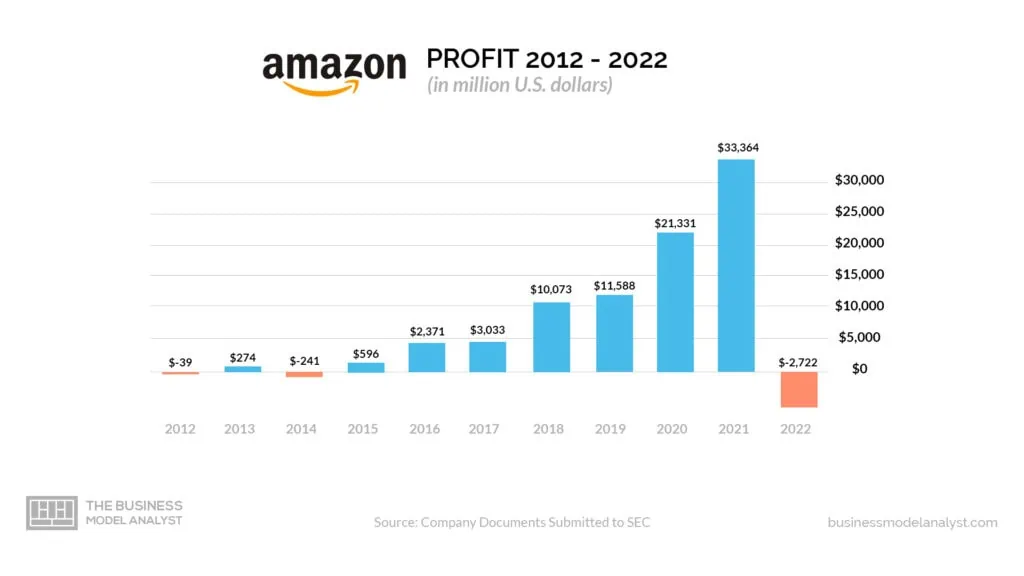
While Amazon wasn’t profitable in 2022, its prior profitability was rooted in its rapid revenue growth over the past decade. As Amazon has expanded into new markets, introduced innovative products and services, and leveraged its scale economies for competitive advantages, the company has seen its sales continue to grow.
By controlling costs even as revenue grows, Amazon can offer low prices while still posting solid profits. This cost control is achieved through efficient operations, leveraging technology, keeping inventory levels low, and investing in automation capabilities. Additionally, Amazon’s huge customer base allows it to benefit from marketing services or cloud computing services offered to third parties.
Analysis of disruptive impact on the traditional and modern commerce industry
Amazon has had a massive influence on both the traditional retail market and the e-commerce industry. Prior to the emergence of Amazon, the e-commerce industry was much smaller in scale and reach. Amazon’s online platform allowed merchants to connect with a significantly larger consumer base with its convenience and easy-to-use services. Additionally, it provided vendors with powerful tools for managing inventory, processing payments, and completing orders that enabled rapid business growth.
The significant success of Amazon’s e-commerce platform has caused a reformation in the way traditional retail does business; retailers have been forced to adopt digital platforms to offer more competitive pricing. This steady transition from brick-and-mortar shops and conventional practices to digital stores has led more companies to embrace technology-based services as an indispensable part of their operations.
Impact on the cloud industry
Amazon has completely revolutionized the cloud industry. Before Amazon, large technology companies such as Microsoft, Oracle, and IBM provided cloud services, but Amazon’s launch of its AWS platform in 2006 changed everything. Instead of fixed prices for each customer, AWS allowed customers to customize their usage and pay only for what they used on a pay-as-you-go basis. This had a massive impact since it gave customers more control over what they paid for. Consequently, AWS quickly gained dominance in the market and now accounts for almost half of the global cloud market share.
Because of the success of AWS, cloud providers were forced to become more competitive with regard to cost and features, or face the risk of being left behind. Moreover, this opened up space in the industry for new players like Google Cloud and Azure, which may not have been possible without Amazon’s influence.
Amazon Business Financials
Over the years, Amazon has seen a tremendous amount of growth in both its sales and profits. In 2015, Amazon reported $107 billion in revenue and $596 million in net income. By 2018, these figures had grown significantly to $233 billion in revenue and $10 billion in net income, respectively. Additionally, operating cash flow grew from $12 billion in 2015 to $30.7 billion in 2018. This increase was due largely to cost-cutting measures as well as Amazon’s ability to leverage its scale and infrastructure for greater efficiency.
The expansion of Amazon’s profitability can also be seen through an increased operating margin rate, from 0.31% in Q1 2015 up to 6.63% by 2021; this indicates that more of every dollar earned is being kept within the business rather than spent on expenses or taxes each year, allowing for further growth potential both organically and externally (via acquisitions).
Potential for Profitability
Amazon is an exceptional company that has shown consistent and strong financial performance for many years. It has achieved this through its diverse range of services, which allow it to exploit a wide variety of markets, as well as by investing in innovation and technology. By providing an intuitive platform for e-commerce, Amazon has revolutionized the way people shop, making it more convenient and efficient than ever before.
In addition to this, Amazon continues to pursue opportunities to expand into new markets and develop innovative products, such as its purchase of Whole Foods or the cloud industry. Its sophisticated algorithms have also enabled it to remain competitive in offering prices that customers can trust while still keeping costs low — another reason why Amazon is so successful and profitable.
Challenges that Amazon faces as a business
Amazon is a highly successful business; however, there are still several challenges it is facing that could reduce its profitability.
Most significantly, competition in the e-commerce and cloud services markets has increased dramatically, with companies such as Walmart and Target posing significant threats.
Amazon also must cope with rising costs for consumer services such as delivery fees and face potential regulation from governments that are concerned about the company’s market power.
Furthermore, profit margins have been steadily decreasing due to investments in new products and services, while the company is under pressure from labor groups citing long work hours, low pay, and a lack of job security.
Despite these obstacles, Amazon is well-positioned economically, which should allow it to remain productive and profitable into the future.
Conclusion
Amazon has had incredibly successful results throughout its history, and its upward trend in profits continues. It has been able to achieve this success through its diverse offerings of products and services that appeal to many different customers, along with the utilization of technologically advanced methods for better utilizing its resources. Its advancements have led it to become one of the most successful businesses in today’s market.
In spite of some recent declines in profit margins due to heightened competition as well as expenses related to implementing new ventures and investments, Amazon still maintains a great deal of potential for continued profitability growth moving forward.


