The Facebook business model is a multisided platform. Although other brands have called themselves “social networks” before, such as MySpace or Orkut, it’s fair to say that the first to turn this digital environment into a successful business model is, no doubt, Facebook. With over 15 years in the market, Facebook now has more than 2 billion users all over the world, and it keeps active and growing.
Also, due to the acquisitions that the company has been taking on brands — and competitors as well —, like Instagram and WhatsApp. In spite of all the speculation about selling users’ data, Mark Zuckerberg, Facebook’s founder, states that this has never been — and never will — the network’s revenue stream. Even because it wouldn’t be financially healthy for its own business. But, if that’s true, then what’s Facebook’s Business Model? How does Facebook make money? Let’s take a closer look.
Contents
More than a social network
According to Zuckerberg, as he was developing Facebook, he wouldn’t have the ambition to build a worldwide enterprise. Unlike that, he would only realize that one “could find almost anything on the internet — music, books, information — except the thing that matters most: people”. Nowadays, Facebook has several other companies under its “umbrella”. Among them, there are Instagram, WhatsApp, Oculus (virtual reality tech), Moves (step counter app), and more.
A brief history of Facebook
Facebook’s history goes back to 2003, when the founders Mark Zuckerberg, Eduardo Saverin, Dustin Moskovitz, and Chris Hughes were studying at Harvard University. It began as an online service where students would judge each other’s appearance, called Facemash — but it was shit down on only two days, for violating some policies. In January of the next year, the four of them developed thefacebok.com, a social network for Harvard students to post photos and personal information.
As its popularity grew, thefacebook.com was open for students from other institutions to join. By the end of 2004, over one million people had registered and, in the same year, companies such as MasterCard offered to pay for advertising on the website.
In 2005, the social network removed the “the” and became only Facebook, and high-schoolers and students from outside the United States were allowed to join. That enabled the website to jump to six million users.
The next year, anyone above 13 years of age would be welcome. In 2008, Facebook surpassed MySpace and, four years later, it became a public company, with its initial IPO raising $16 billion, which lead its valuation to $102.4 billion.
Who Owns Facebook
Facebook is owned since its foundation by Mark Zuckerberg, through its holding group, Facebook Inc. After acquiring Instagram and WhatsApp, Zuckerberg decided it was better to rename the holding group to separate the Facebook social network from the group. So, in October 2021, Facebook Inc. was relabeled to Meta Inc., with Zuckerberg as its CEO and owner of all the companies of the group.
Facebook’s Mission Statement
Facebook’s mission is to give people the power to build community and bring the world closer together.
How Facebook makes money
The great revenue stream of Facebook is the targeted advertisement, due to the benefit that the platform offers, of allowing the advertisers to reach their target audience, through information the network collects from its users. And, according to Zuckerberg, that’s precisely why it wouldn’t make any sense for Facebook to sell its users’ data. It would be cutting its own throat, as the platform would be handing over its greatest differential.
Soon, the advertisers wouldn’t need Facebook anymore. Facebook’s trump card is exactly to permit its advertisers to invest money in the right audience. Within more than 2 billion profiles, the businesses are able to have their products/services viewed only by American 25-30-year-old females, who have a degree and are interested in marriage, for example.
That’s the way advertisement became accounting for 97% to 99% of Facebook’s revenue. The other 3% or less is made up of payments received by games played and products sold on the platform, private social network services to businesses, and other products offered by each of the brands under its umbrella, such as Oculus, a Virtual Reality device.
Facebook’s Business Model Canvas
Let’s see what the Facebook’s business model canvas looks like:
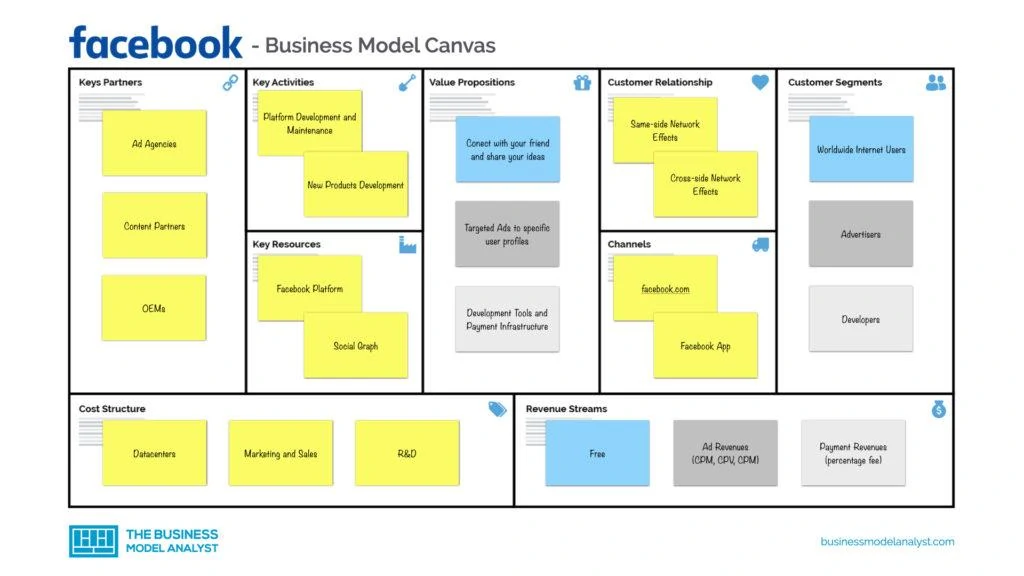
Facebook’s Customer Segments
- Users: They are the biggest customer segment of Facebook, and stand for one-third of the world’s population! They are all the people who have their profiles in the network and use them to interact and communicate with friends and other people with similar interests around the globe. They don’t pay Facebook anything and, thus, they are not directly responsible for the business revenue. However, they are the basis that makes Facebook interesting for the ones who do pay;
- Businesses and advertisers: This is the segment involved in Facebook’s revenue. It encompasses all the brands and businesses that advertise on the social network. They pay to have ads for their products and services on the platform, which, from its side, offers a more qualified audience. Due to the information that Facebook collects from its users, the company is able to target advertisements on its platform, allowing brands and businesses to have their ads viewed by its target audience. Anyway, although these are the revenue providers, they will only keep their interest as long as the non-paying user base is wide and qualified;
- Developers: It’s the smallest customer segment, and it includes the ones who develop apps and games through Facebook’s platform.
Facebook’s Value Propositions
As Facebook has three diverse customer segments, each segment will perceive the brand’s value differently. That said, let’s divide the value proposition by segment:
- For users: The greatest benefit is to keep in touch with family and friends, via text and picture posting, and by interactions through comments and direct messages. This is especially relevant for the ones who travel a lot or live far from their loved ones. Another advantage is the availability of entertainment and information. Facebook is useful both for those who want to get entertained by the lives of their acquaintances and for people who use it as a source of news and current affairs;
- For advertisers: The possibility of targeted campaigns, focused on their particular target audience, has been of great value for brands. By achieving greater penetration in its main audience, companies also get greater engagement in their customer segment of interest. Another relevant point, especially for small businesses or young companies is that the tools to advertise on Facebook are quite simple, in the best “do it yourself” style, which reduces the need to hire someone to develop their own advertising content;
- For developers: Facebook is an amazing platform for developing apps and games, and it offers a wide range of views and disclosure. Besides, there is a great network of providers for advertisement services.
Facebook’s Channels
It’s quite clear that the main distribution channels of Facebook are its own website and app, because that’s where users find each other, and advertisers access their audience. Inside that, the channels can be divided into feed, notifications, direct messages, and stories. Other channels include the app stores, other products of the company, e.g. Instagram and WhatsApp, and, of course, word of mouth power.
Facebook’s Customer Relationships
Facebook’s customer relationship is based on its own platform, which is very user-friendly, as it allows users to specify their profile configurations and use them with no hard time. In addition, Facebook has an international sales organization, that works alongside marketing and advertising agencies, to attract advertisers.
Facebook’s Revenue Streams
- Payment revenues (percentage fees)
- Ad revenues (CPM and CPV)
- Free
Facebook’s Key Resources
Within Facebook’s key resources, the only tangible one (but essentially digital) is its platform, which demands technological infrastructure. Aside from that, the other key resources are the network users and their content production, and the Facebook brand. The active users are the company’s biggest asset. Because, if there aren’t users, there is no audience to view the ads. And to make them engaged, there must be relevant content, to avoid churn. As for the brand, it’s a very powerful name, still the great synonym for “social network”, indeed.
Facebook’s Key Activities
Above all key activities, it is the platform development and maintenance, in order to ensure a positive experience and avoid negative effects on the social network. Then, besides all the infrastructure that the website demands, to keep it working properly and optimized 24/7, Facebook also needs to invest in good practices and control bad behavior within the network. Furthermore, the company focuses on user acquisition and engagement, data and information storage and security, talent hiring and retaining, and sales and marketing.
Facebook’s Key Partners
- Content developers, e.g. videos, games, texts, etc.
- Developers for compatible operating systems, browsers, and hardware
- Digital influencers
- Businesses and brands that advertise or directly sell on the platform
- Marketing agencies
Facebook’s Cost Structure
The biggest share of Facebook’s cost structure revolves around platform maintenance and its billions of users’ data storage. Besides, there is user CAC (cost of acquisition) by delivering tools that foster user engagement, research and development investment, marketing and advertising, customer support, and all the regular general and administrative expenses of a worldwide company.
Facebook’s Competitors
- Snap: Photo and video sharing app released in 2011, with 280 million active daily users. It is very popular among kids under 16 because the content disappears in seconds;
- LinkedIn: This professional network was launched in 2003. It aims at linking recruiters, employers, and potential applicants. The site is free to use, but it has some premium features, for its over 600 million registered users;
- Twitter: Free microblogging service founded in 2006. Its 180 million members can post short texts called tweets;
- YouTube: The video-sharing platform allows users to upload, view, and share videos. It was founded in 2005 and accounts for 2 billion regular users, who watch more than one billion hours of videos each day;
- Pinterest: This social networking site is for saving and discovering creative ideas. It was created in 2009, and it has around 480 million active users nowadays;
- TikTok: It is a social media app for creating and sharing videos or for live broadcasting. Founded in 2012, it is the newest one and has more than one billion active users currently.
Facebook’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Facebook:
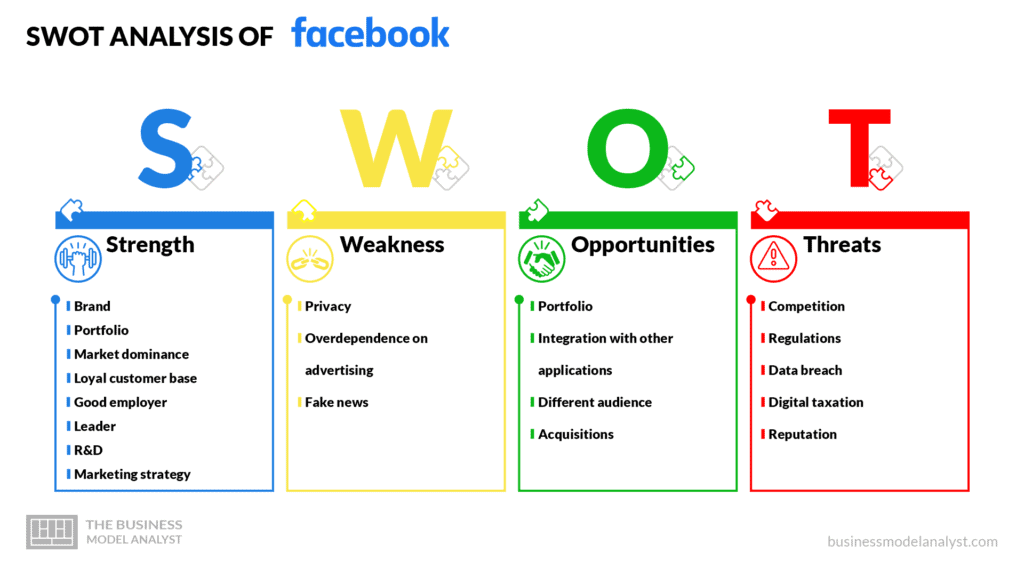
Facebook’s Strengths
- Brand: Yes, Facebook has already been in the top 5 most valuable brands in the world. Now it is the 13th one, but that still represents a very strong name, valued at over $35 billion;
- Portfolio: Diversification and acquisitions allow Facebook to protect its financial assets, as it does not put all its investments in only one sector. WhatsApp, Instagram, Messenger, Oculus, Workplace, Portal, and Calibra stand as major strengths for the business;
- Market dominance: Despite its declining user number, Facebook still remains the leader in the social network industry, with more than 2 billion users. And the 3rd, 4th, and 6th places are occupied by WhatsApp, Messenger, and Instagram, respectively, which are part of the company;
- Loyal customer base: Around 30% of the world’s population uses Facebook and its family products (Instagram, WhatsApp, Messenger) putting the company in a very comfortable position;
- Good employer: HR policies put Facebook as one of the best employers in the world, thus attracting and retaining top talent;
- Leader: Mark Zuckerberg is a brand itself nowadays. His visionary leadership provides innovation, stability, and sustainability for the business;
- R&D: Facebook is one of the leaders worldwide in Research and Development investments, focusing almost 20% of its total revenue on innovation;
- Marketing strategy: Facebook is a very powerful marketing tool, as it reaches 2 billion people but enables target advertisement. That is why 97% to t99% of its revenue comes from ads.
Facebook’s Weaknesses
- Privacy: Facebook faces some decline in popularity and a bad reputation due to its lack of protection regarding users’ privacy and data;
- Overdependence on advertising: The business revenue is totally dependent on social media (the other brands of the family are in the same industry) and, as mentioned above, advertisement is basically the source of revenue for the business, leaving no place for other revenue streams;
- Fake news: Facebook has been under huge critics as a result of its incapacity for controlling misleading information.
Facebook’s Opportunities
- Portfolio: Facebook has the potential and resources to diversify its portfolio in order to avoid overdependence on social media and advertising;
- Integration with other applications: Facebook can be open to integration with many types of applications, such as e-commerce, podcasts, games, etc.;
- Different audience: With new features, Facebook can attract other target segments, besides tech-savvy youngsters;
- Acquisitions: Facebook has the potential to keep acquiring other companies, even from different industries.
Facebook’s Threats
- Competition: Facebook’s user number is declining, and much as a result of competition with old platforms as well as new entrants;
- Regulations: There are many new regulations regarding the Internet that can harm Facebook’s business model, such as ones concerning data safety, user privacy, intellectual property, etc.;
- Data breach: Data breaches can affect millions of users, by exposing personal information to the dark web;
- Digital taxation: This new tax is being adopted in the UK and European Union. If this kind of tax is implemented in other countries, it can jeopardize Facebook’s profits;
- Reputation: Data breaches, fake news, hacked and/or false accounts, and other scandals have tainted Facebook’s reputation, thus reducing usage.
-> Read More About Facebook’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Despite all the accusations and controversies, Facebook is still booming. Although many people believe this social network is going to end soon, Facebook’s brand and business are going to certainly remain, investing in new approaches and brand names, as you may have noticed.

