The eBay business model revolves around a marketplace where buyers can bid on items or purchase them directly from sellers. eBay is an online marketplace that allows people to buy and sell goods. The company was founded in 1995 and has since grown to become one of the world’s largest e-commerce platforms, with millions of users in over 190 countries.
In addition to its marketplace, eBay also offers other services to its users, such as payment processing, financing, and advertising. The company makes money through various revenue streams, including fees from sellers, advertising, and partnerships with other companies. eBay has a diverse customer base, including individuals and businesses of all sizes.
The company also has partnerships with various retailers and technology companies to expand its reach and offerings. eBay faces competition from other online marketplaces, such as Amazon and Alibaba, as well as traditional brick-and-mortar retailers. Despite this, eBay has continued to grow and evolve its business model to stay competitive in the e-commerce market.
Contents
A brief history of eBay and The Reason Behind Their Success
eBay was founded in 1995 by Pierre Omidyar, a French-born computer programmer. The company’s initial goal was to create a platform where individuals could buy and sell items to each other directly. However, Omidyar quickly realized that the real potential of the platform was in its ability to facilitate auctions. This allowed people to bid on items, driving up their prices and giving sellers the opportunity to earn more money for their goods.
eBay’s unique business model proved to be incredibly successful. By 1997, the company had over one million registered users, and it continued to grow at an impressive rate. In 1998, eBay went public and became a publicly-traded company.
One of the key reasons behind eBay’s success was its low fees. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar auction houses, which often charge high commissions, eBay only charges a small fee for each listing. This made it an attractive option for both buyers and sellers. Additionally, eBay’s online platform made it easy for people to search for and bid on items, even if they were located far away from the seller.
Another reason behind eBay’s success was the way it embraced the internet and leveraged its capabilities. By allowing sellers to list their items online and enabling buyers to bid on them, eBay created an efficient and accessible marketplace that appealed to a wide range of users.
In the early 2000s, eBay expanded its business by acquiring a number of other companies. In 2002, the company acquired PayPal, a popular online payment platform, which allowed eBay users to easily and securely make payments for their purchases. In 2005, eBay acquired Skype, a popular internet-based communication platform that allowed users to communicate with each other in real time. These acquisitions helped to strengthen eBay’s position as a market leader and further enhanced its appeal to users.
Today, eBay is one of the largest and most successful online marketplaces in the world. With over 182 million active users and millions of items listed for sale, it remains a popular destination for both buyers and sellers. While the company continues to face competition from other online marketplaces, its unique business model and strong brand recognition have helped it to maintain its position as a leader in the industry.
Who Owns eBay
eBay is now a publicly-owned company, with the majority of its shares held by mutual fund holders at 49.23%. The Vanguard Group, Inc. is the largest institutional shareholder with a 10.77% stake, followed by BlackRock Fund Advisors with 5%. Individual stakeholders own 11.33% of eBay, while other institutional holders own the remaining 39.83%.
eBay Mission Statement
eBay’s mission statement is “to provide a global online marketplace where practically anyone can trade practically anything, enabling economic opportunity around the world.”
How eBay makes money
eBay makes money through the fees that it charges users for listing and selling items on its platform. It also generates revenue from advertising and through its payment processing services. Additionally, eBay has a growing e-commerce business that allows it to sell products directly to consumers. These various streams of revenue allow eBay to continue to grow and expand its business.
Categorically, eBay makes money in these ways:
- Fees from listing and selling items on the platform;
- Advertising fees from eBay’s marketing services;
- Revenue from subsidiaries*.
*While PayPal can be considered a subsidiary of eBay, the company decided on September 30, 2014, to “spin off PayPal into a separate publicly traded company.”
A few other ways that eBay makes money, as well as a breakdown of the above categories, are given below:
- Listing fees: eBay charges sellers a fee to list their items for sale;
- Final value fees: eBay collects a percentage of the final sale price when an item sells;
- Promoted listings: eBay charges sellers an additional fee to have their listings appear higher in search results and other prominent locations on the site;
- eBay Plus subscription: eBay offers a paid subscription service called eBay Plus, which provides customers with additional benefits such as free shipping and exclusive deals;
- Advertising: eBay generates revenue through the display of product ads leading to external online retail websites;
- StubHub: eBay owns the online ticket marketplace StubHub, which makes money through listing and transaction fees;
- Other ventures: eBay also generates revenue through its investments in and partnerships with other companies.
Fees from listing and selling items on the platform
eBay makes money from fees charged to users for listing and selling items on its platform. These fees are typically a percentage of the final sale price and vary depending on the item’s category and the seller’s status on the platform. For example, a standard seller may be charged a 10% fee for selling a piece of clothing, while a power seller (a high-volume seller with a good reputation on the platform) may be charged a lower fee of 6%. These fees provide a significant source of revenue for eBay.
Advertising fees from eBay’s marketing services
eBay makes money from advertising fees by charging advertisers for the ability to promote their products on eBay’s platform. This allows advertisers to reach a large audience of potential customers who are actively using eBay to search for and buy products. When a user clicks on an advertiser’s ad, the advertiser is charged a fee, which generates revenue for eBay. Additionally, eBay may offer additional marketing services, such as featured listing placements or promotional emails, for which advertisers can pay additional fees.
Revenue from subsidiaries
eBay makes money from its subsidiaries, such as StubHub, by earning a portion of the revenue generated by these businesses. StubHub is an online ticket marketplace that allows users to buy and sell tickets for sports, music, and other live events. When a user buys a ticket on StubHub, the company charges a fee for its services. This fee generates revenue for StubHub, and since eBay owns StubHub, a portion of that revenue goes to eBay as well. In this way, eBay can generate additional revenue by leveraging the success of its subsidiary companies.
eBay Business Model Canvas
The eBay Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
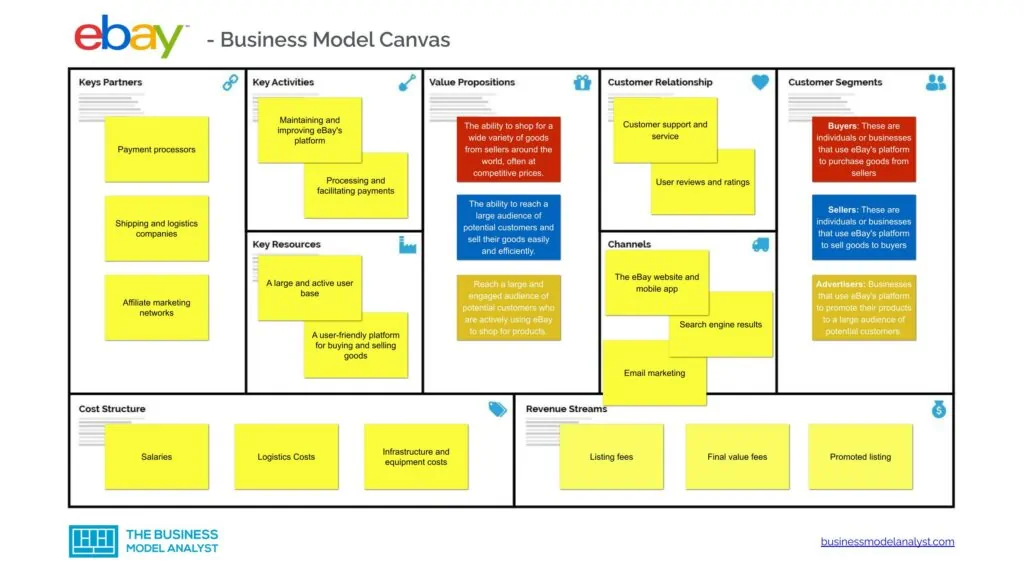
eBay Customer Segments
eBay’s customer segments consist of:
- Buyers: These are individuals or businesses that use eBay’s platform to purchase goods from sellers;
- Sellers: These are individuals or businesses that use eBay’s platform to sell goods to buyers;
- Advertisers: These are businesses that use eBay’s platform to promote their products to a large audience of potential customers. They may pay for additional marketing services, such as featured listings or classified ads, to increase the visibility of their products on eBay’s platform.
eBay Value Propositions
eBay’s value propositions consist of:
- For buyers: eBay’s value proposition is the ability to shop for a wide variety of goods from sellers around the world, often at competitive prices. eBay also offers features such as buyer protection and easy returns to make the shopping experience more convenient and secure;
- For sellers: eBay’s value proposition is the ability to reach a large audience of potential customers and sell their goods easily and efficiently. eBay also offers features such as seller protection and payment processing to make the selling experience more convenient and secure;
- For advertisers: eBay’s value proposition is the ability to reach a large and engaged audience of potential customers who are actively using eBay to shop for products. eBay also offers additional marketing services to help advertisers increase the visibility and effectiveness of their advertising on eBay’s platform.
eBay Channels
eBay’s channels consist of:
- The eBay website and mobile app
- Search engine results
- Email marketing
- Social media advertising
- Affiliate marketing programs
- Partnerships and collaborations with other companies
- Online ads
- Offline advertising, such as television or print ads
eBay Customer Relationships
eBay’s customer relationships consist of:
- Customer support and service
- User reviews and ratings
- Social media
- Community forums
- Subscription services
- Loyalty programs and rewards
- Personalized product recommendations
- Network Effects
eBay Revenue Streams
eBay’s revenue streams consist of:
- Listing fees
- Final value fees
- Promoted listing
- eBay Plus subscription
- Advertising
- Subsidiaries
eBay Key Resources
eBay’s key resources consist of:
- A large and active user base
- A user-friendly platform for buying and selling goods
- A robust and secure payment processing system
- A team of employees with expertise in e-commerce, technology, and customer service
- Data and algorithms for personalized product recommendations and targeted advertising
- Physical infrastructure for storing and processing data
- Intellectual property, such as trademarks and patents.
- Partnerships
- Affiliates
- Brand Reputation
- Auction-style listings
eBay Key Activities
eBay’s key activities consist of:
- Maintaining and improving eBay’s platform
- Processing and facilitating payments
- Providing customer support
- Marketing and advertising
- Developing and implementing technology and algorithms
- Managing relationships with subsidiaries and partners
- Protecting intellectual property and ensuring compliance.
- Shipping
- Logistics
- Bidding Process
eBay Key Partners
eBay’s key partners consist of:
- Payment processors
- Shipping and logistics companies
- Affiliate marketing networks
- Subsidiaries, such as StubHub
- Strategic partners and collaborators in the e-commerce industry
- Vendors
- Investors
eBay Cost Structure
eBay’s cost structure consists of:
- Salaries
- Logistics Costs
- Infrastructure and equipment costs
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Payment processing fees
- Costs associated with maintaining and improving the eBay platform
- Legal and compliance costs
- Fees for partner and collaborator services
- Customer Service
eBay Competitors
- Amazon: Amazon is a large, global e-commerce company that offers a wide variety of products and services, including online marketplaces for buying and selling goods. Amazon’s platform is known for its extensive selection of products, competitive pricing, and fast delivery options. The company also offers services such as Amazon Prime, which includes free shipping and access to streaming media, and Amazon Marketplace, which allows third-party sellers to reach Amazon’s large customer base.
- Alibaba: Alibaba is a Chinese e-commerce company that operates a platform for wholesale and retail trade, as well as other services such as cloud computing and digital media. Alibaba’s platform is used by businesses of all sizes to buy and sell goods and services, and the company has a strong presence in the Asian market. Alibaba also operates the popular online shopping site Taobao and the business-to-business platform Alibaba.com.
- Walmart: Walmart is a large, multinational retailer that operates both brick-and-mortar stores and an online marketplace. Walmart’s online platform offers a wide variety of products at low prices, and the company also offers services such as in-store pickup and grocery delivery. Walmart’s physical stores give it a significant advantage in terms of distribution and logistics, and the company has a strong presence in the U.S. market.
- Etsy: Etsy is a website where you can buy handmade and vintage items. The platform is popular with small businesses and individual sellers who offer unique, handmade, or vintage items. Etsy’s focus on handmade and vintage products sets it apart from other online marketplaces, and the company also offers services such as personalized recommendations and support for sellers.
- Wish: Wish is a mobile-based e-commerce platform that offers a wide variety of products at low prices. Wish’s platform is known for its focus on low-cost items, and the company uses algorithms and data to personalize product recommendations and target ads to individual users. Wish also offers features such as price tracking and coupons to help users save money on their purchases.
- Rakuten: Rakuten is a Japanese e-commerce company that operates online marketplaces and offers other services such as cashback rewards and digital media. Rakuten’s platform is popular in Japan and other parts of Asia, and the company’s cashback rewards program is a major differentiator.
eBay SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of eBay:
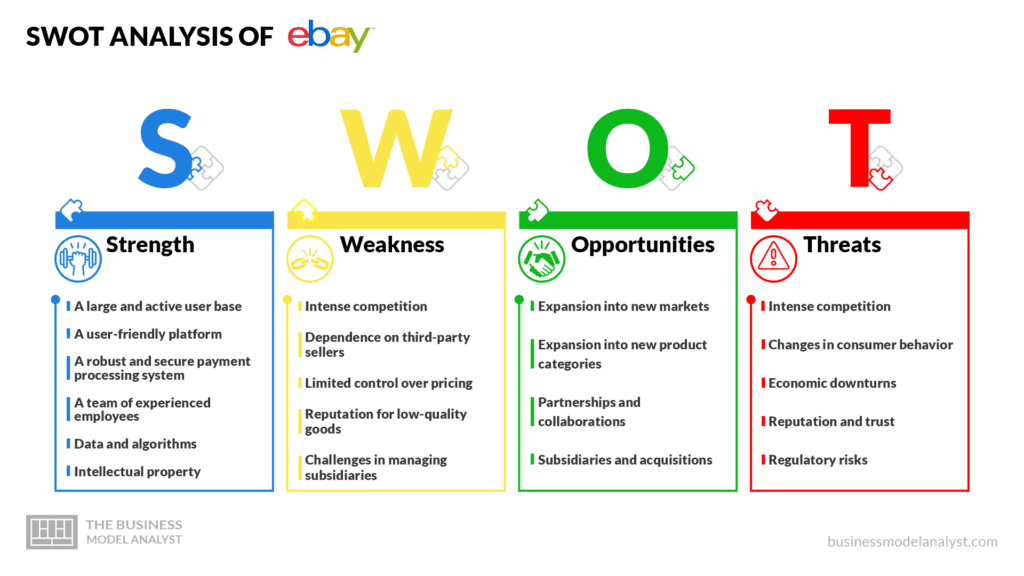
eBay Strengths
- A large and active user base: eBay has millions of users around the world who buy and sell goods on the platform, which gives it a strong network effect and makes it an attractive destination for buyers and sellers;
- A user-friendly platform: eBay’s platform is easy to use and offers features such as personalized recommendations and detailed product listings to help users find what they’re looking for;
- A robust and secure payment processing system: eBay’s payment processing system is secure and reliable, which helps to build trust and confidence among users;
- A team of experienced employees: eBay has a team of employees with expertise in e-commerce, technology, and customer service, which helps to maintain and improve the platform and support users;
- Data and algorithms: eBay uses data and algorithms to personalize product recommendations and target advertising to individual users, which can improve the user experience and drive sales;
- Intellectual property: eBay has a portfolio of intellectual property, such as trademarks and patents, which can help to protect its brand and prevent competitors from copying its innovations.
eBay Weaknesses
- Intense competition: eBay faces intense competition from other online marketplaces and e-commerce platforms, which can make it difficult for the company to differentiate itself and maintain its market share;
- Dependence on third-party sellers: A significant portion of the goods sold on eBay are provided by third-party sellers, which means that the quality and reliability of those goods are outside of eBay’s control. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction and damage eBay’s reputation;
- Limited control over pricing: Since eBay’s platform is an open marketplace, sellers are free to set their own prices for the goods they offer. This means that eBay has limited control over pricing and may be unable to offer the lowest prices for certain products;
- Reputation for low-quality goods: In the past, eBay has been associated with low-quality goods and counterfeit items, which can damage its reputation and make it less appealing to buyers;
- Challenges in managing subsidiaries: eBay owns a number of subsidiaries, such as StubHub, which can add complexity to the company’s operations and make it difficult to achieve synergies and efficiencies.
eBay Opportunities
- Expansion into new markets: eBay has a strong presence in many markets around the world, but there are still many potential markets where the company could expand. For example, eBay could look to enter emerging markets with large and growing populations, such as India and Indonesia, or expand its presence in existing markets by offering new products or services;
- Expansion into new product categories: eBay offers a wide variety of goods, but there are still many product categories where the company could expand. For example, eBay could look to offer more services, such as home cleaning or appliance repair, or expand into new areas, such as groceries or home furnishings;
- Partnerships and collaborations: eBay could look to partner with other companies or organizations to expand its reach and offer new products or services. For example, eBay could partner with retail chains to offer in-store pickup for online orders, or collaborate with manufacturers to offer exclusive products or discounts;
- Subsidiaries and acquisitions: eBay could look to grow through acquisitions or the expansion of its existing subsidiaries. For example, the company could acquire other online marketplaces or e-commerce platforms to expand its reach, or invest in its subsidiaries, such as StubHub, to grow those businesses.
eBay Threats
- Intense competition: eBay faces intense competition from other online marketplaces and e-commerce platforms, which can make it difficult for the company to differentiate itself and maintain its market share. These competitors may have competitive advantages in areas such as product selection, pricing, delivery speed, or customer service, which can make it difficult for eBay to compete;
- Changes in consumer behavior: The e-commerce industry is rapidly evolving, and consumer behavior is constantly changing. If consumers shift away from using online marketplaces like eBay in favor of other shopping channels or platforms, eBay’s business could be adversely affected;
- Economic downturns: Economic downturns can lead to reduced consumer spending, which can impact eBay’s business. If consumers are more cautious about their spending during an economic downturn, they may be less likely to buy and sell goods on eBay’s platform, which could impact the company’s revenue and growth;
- Reputation and trust: eBay’s reputation and the trust of its users are crucial to the company’s success. If eBay fails to protect its users’ personal information, resolve disputes effectively, or prevent the sale of counterfeit or low-quality goods, its reputation could be damaged, and users may be less likely to use the platform;
- Regulatory risks: As a large and influential company, eBay is subject to regulatory scrutiny and may face fines or other penalties if it fails to comply with relevant laws and regulations. This can be a significant risk for the company and can damage its reputation.
Conclusion
eBay is a successful online marketplace that allows buyers and sellers to easily connect and conduct transactions. The company’s business model is based on generating revenue through fees charged to sellers and advertisers, and it also leverages its subsidiaries to generate additional revenue. eBay has strengths, such as a large and active user base, but it also faces competition and regulatory risks. The company has opportunities for growth, such as expansion into new markets and product categories, but it must also address threats to maintain its success.

