Even in the face of rising competition, annual reports continue to reveal that Costco Wholesale Corporation keeps growing. This is irrefutable proof that the Costco business model still works. Here, we’ll be doing a concise analysis of the multinational retail firm to see how it has been able to maintain a competitive edge and expand while retaining long-term viability in the 21st century.
Contents
A brief history of Costco
Costco began in 1976 when Sol and Robert Price opened what would be the first exclusive warehouse for business shoppers. Over the next three years, Price Club would grow to have more than 200, 000 members and $1 million in profit.
The first Costco warehouse (with Price Club as its parent company) was opened in Seattle, Washington in September 1983. Price Club and Costco merged in 1993 to become Price Costco. Four years later, the name of the firm was finally changed to Costco Companies, Inc.
By the early 21st century, Costco had spread from America to Mexico, Canada, Australia, Europe, and the Far East.
Today, beyond the outstanding prices Costco discount stores are known for, they’ve also become very popular for offering their employees better pay and dividends, compared to many of their counterparts in the retail industry.
Who Owns Costco
Costco is currently owned by the Costco Wholesale Corporation. The current CEO of the business franchise is W. Craig Jelinek. He has been in the position since January 1, 2012. Another noteworthy face in the leadership of the organization is its incumbent chairman, Hamilton E. James. All critical decisions influencing the operation and future of Costco are jointly made by the CEO and major stakeholders of the corporation.
Costco’s Mission Statement
The mission statement of Costco Wholesale Corporation is, “To continually provide members with quality goods and services at the lowest possible prices.” This byword is particularly apt, as it simplifies and highlights how the Costco business model and strategy are set up and executed.
Just as the statement implies, Costco places a high emphasis on quality and cost leadership. As these two elements are what most consumers look for in a retail market, they’re able to effectively ensure that their brand continually appeals to its target audience.
Consequently, Costco’s mission statement reveals its main competitive edge in the industry.
How Costco makes money
Over the years, Costco has managed to efficiently diversify its income stream through exploring multiple investment channels. So, while the main means of profit for the company is selling products at high discount rates to its members, there are many other sources of revenue for Costco. Here are all of them in detail.
Merchandise Sales Volume
More than 90% of the company’s income stems from the sale of in-store Stock Keeping Units (SKUs). By keeping and selling only 3,700 units in its warehouse at any given point, Costco has been able to generate more than $150 billion in annual income.
Some of the categories that the brand offers goods range from Food and Sundries to Ancillaries, Fresh Foods, Softlines, and Hardlines.
Membership Fees
Costco differs from many conventional warehouses in that you have to be a member before you can leverage the bargain prices that they offer. This membership attracts a fee. Also, membership fees can vary as the company operates a tier system.
Unlike many other brands, Costco has been able to find a way around its membership requirement being a barrier to entry. Because of this, it’s been able to accrue more than 114 million members. The membership fees generated as a result account for more than 2% of the company’s annual income.
E-commerce Offers and Sales
The Costco e-commerce platform was launched in April 2001. Since that time, it has become one of the most patronized online retailers in the U.S. It also has the special benefit of helping Costco members save money without having to enter the company’s brick-and-mortar warehouses.
Auto Sales Program
By partnering with more than 3, 000 dealerships, Costco members can also purchase new or used vehicles through this program. This helps them get the automobiles at discounted prices with several value-added perks as well.
Home and Installation Programs
The company also gets a steady stream of revenue by offering its members numerous home and installation services like countertop installation, HVAC installation, and carpet and flooring installation.
Costco’s Business Model Canvas
The Costco business model can be broken down and efficiently analyzed using the business model canvas below.
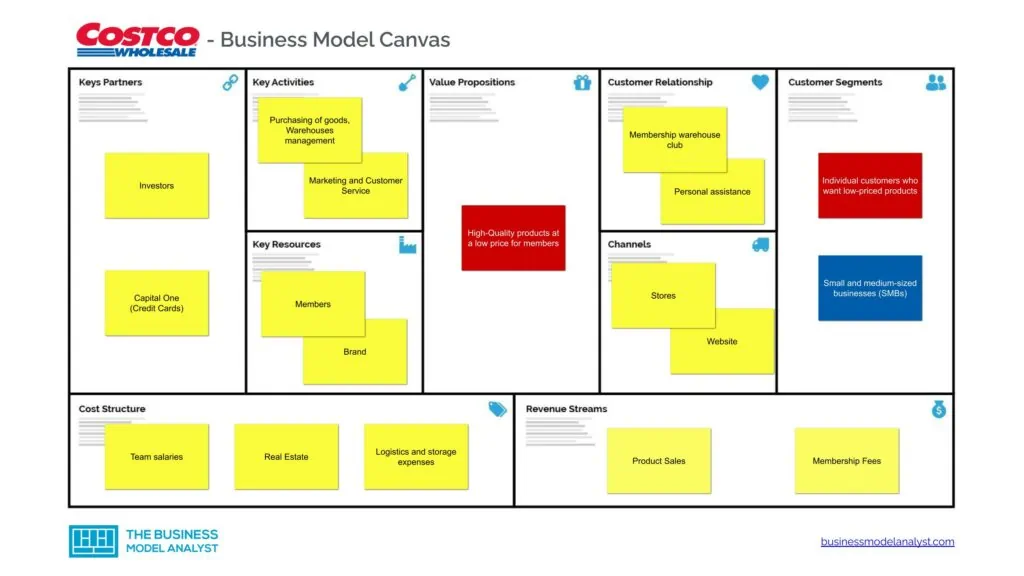
Costco’s Customer Segments
Like every other customer-centric brand, Costco’s business model is heavily reliant on its consumers. This is because the more customers are given a better spending platform, the more revenue is likely to be generated.
To that end, there are two categories of membership offered by this brand. These are:
- Gold Star Membership: This membership category is designed to cater to the needs of individual customers who specifically want to benefit from the high discount prices offered by the company;
- Business Membership: This type of membership is designed for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). It’s set up to help optimize the resale of Costco goods by these outlets. Outside SMBs, individuals who have a business license or evidence of business ownership are also eligible for this membership type. In addition to this, the company also offers Executive Memberships. This allows customers to collect points and earn rewards as they perform certain activities or transactions with Costco.
Costco’s Value Propositions
Costco has especially strong value propositions. The value-added goods and services that it offers its members hinges on four elements. These are:
- Low Prices: As Costco operates a unique business model that focuses on offering wholesale prices for merchandise, members will almost always get lower prices when shopping at its warehouses. This makes Costco more attractive than conventional grocery stores and supermarkets;
- Zero Risk Membership: Another strong aspect of its value proposition is its risk-free membership offering. The fact that consumers are given the option of claiming a refund if unsatisfied with Costco’s service is a major selling point. In addition to this, members can also turn in several goods in-store and request a refund, further contributing to higher customer confidence in the brand;
- Membership Reward Program: Costco’s Executive Memberships reward scheme which allows customers to claim up to $750 annually in reward points has also been proven to have a strong positive effect on the brand’s exposure;
- International Exposure: Costco’s global reach and growing online sales channel means that members can always readily access the goods and services offered by the merchant.
Costco’s Channels
The company operates three main channels. These are:
- Its International Chain of Wholesale Warehouses: As of 2021, Costco had 825 membership warehouses worldwide. This chain of warehouses accounts for the majority of the sales and revenue generated by the company;
- The Costco Website: This provider uses is its official website, www.costco.com. Through this platform, customers can find information on elements like running reward schemes, the location of warehouses, and membership options;
- Online Sales Channel: This platform offers various products and services, a few of which mightn’t even be available in the company’s brick-and-mortar stores. However, the reach of this online platform is still quite limited, as it’s currently only available in locations like the U.S., Mexico, Canada, and the United Kingdom.
Costco’s Customer Relationships
Costco maintains its customer engagements through:
- Social media
- In-person sales support service
- Email relations
- Membership warehouse club
- An optimized self-service platform (This channel is currently only available in certain regions)
Costco’s Revenue Streams
Costco’s revenue stream can be broadly divided into two categories. These are:
- Product Sales: This refers to the income accrued from the direct sale of products and services through Costco’s brick-and-mortar stores and online platforms. In 2021, revenue from this outlet totaled more than $170 billion;
- Membership Fees: This refers to the revenue generated from the various types of membership packages offered by the company. In 2021, membership revenue for the company rose to $3.8 billion.
Costco’s Key Resources
This company has five key resources. These are:
- Its vast network of physical warehouses
- Its online store and high-tech IT infrastructure
- Its optimized freight logistics and distribution network
- Its efficient supply chain and a large group of supply partners
- Its professional personnel
Costco’s Key Activities
The most noteworthy activities of this firm are:
- Operating multiple memberships internationally;
- Operating 7 days a week while making a wide range of products and services consistently available;
- Operating a fully functional online sales platform that gives consumers (in certain locations) additional service features like business delivery, travel, and pharmacy.
Costco’s Key Partners
This company has several key partners. Some of which include:
- Its suppliers
- Non-profit programs
- Advertisement, branding, and publicity companies
- Payment solution providers
- Credit partnerships (Formerly with American Express, now with Visa)
- Other technology companies
Costco’s Cost Structure
As a multinational business franchise, Costco incurs various types of costs. Some of these are:
- Operational costs for managing its multinational network of membership outlets
- IT infrastructure maintenance costs
- Logistics and storage expenses
- Retention of personnel costs
- Acquisition of merchandise expenses
- Administrative costs
- Expenses for startup operations
Costco’s Competitors
- Amazon: Amazon.com was created in 1994 by Jeff Bezos. He initially ran the franchise out of his home in Washington. As of 2021, Amazon’s net worth is over $314 billion. This platform is currently fully operational in 13 countries. However, they ship to more than 100 jurisdictions worldwide;
- Sam’s Club: This franchise was established by Sam Walton in 1983. Similarly to the Costco business model, it aims to deliver high-quality products at budget-friendly prices. Sam’s Club major operates in the United States and Puerto Rico. But, they also have outlets in regions like Mexico, Brazil, and China;
- Target: Target was founded by George D. Dayton in 1902. It has its headquarters in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and boasts a $65 billion net worth currently. This franchise predominantly caters to the U.S. market;
- Walmart: This franchise was also founded by Sam Walton. Established in 1962, this organization is active in 24 countries and has more than 10, 000 outlets and clubs. The net worth of Walmart as of 2021 was more than $429 billion.
Costco’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Costco Business Model:

Costco’s Strengths
- Pricing: It allows the company to offer some of the lowest possible prices for all of the goods and services listed on its official website;
- Operating Structure: The business model allows for a high sales volume that’s equally matched with rapid inventory turnover. As a result, Costco is almost always guaranteed large profits, even though they sell at lower prices;
- Operating Efficiency: The business model the company runs on affords it a higher degree of operating efficiency. Costco’s higher operating efficiency is accomplished through variable cost minimization.
Costco’s Weaknesses
- Market Scope: Its membership-only policy effectively restricts its target market. Because only members can shop with this provider, non-members may start to feel unwelcome at Costco brick-and-mortar stores;
- Inventory Capacity: As the success of Costco’s business model is heavily reliant on providing a specific set of goods and services, it’s relatively easier for competitors with a larger selection of offerings like Amazon and Walmart to lure their customers away.
Costco’s Opportunities
- Expansion: There are readily available markets in developing Asian countries just waiting to be leveraged. Costco’s online platform still has room for growth, and its services and products can be further extended into regions where it doesn’t exist currently;
- Diversification: The company can expand the list of products and services it currently offers. This will increase its appeal to potential consumers who are in search of more variety, boost revenue, and put it on a level footing with some of its competition as well.
Costco’s Threats
- Industry Growth: The rapid emergence of more membership warehouse clubs in many of the overseas markets that Costco is yet to tap;
- Competition: The mounting competition from other major retail firms in the industry.
-> Read More About Costco’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
As a business, Costco Wholesale Corporation is highly viable, effective, and efficient. It remains one of the world’s leading minimal expense pioneers, and everything — from its membership fees to bulk purchases — ensures a steady and growing stream of income for the brand.
As its business model is built around offering affordability, Costco is likely to maintain its dominance in the industry long into the future.

