The Coinbase business model is mainly centered around transaction fees that users must pay for services like buying or selling on the platform. Coinbase is a relatively young company that has found major success in the cryptocurrency exchange market. So, we decided to do another business model analysis. This guide will break down Coinbase’s business model in a way that’s easy to understand. Keep reading.
Contents
A brief history of Coinbase
Coinbase is another company that climbed the crypto-wave early by creating a cryptocurrency exchange platform. Brian Armstrong and Fred Ehrsam are the masterminds who founded Coinbase back in 2012.
Brian was a former Airbnb engineer, who originally founded Coinbase before he teamed up with fellow co-founder Fred Ehrsam, who was a former Goldman Sachs trader.
They both came together to create an accessible platform for buying, selling, and storing cryptocurrency.
Who Owns Coinbase
Coinbase was co-founded by Brian Armstrong and Fred Ehrsam in 2012. Today, Coinbase is a public company, with its CEO Brian Armstrong owning a 20% stake.
Coinbase’s Mission Statement
Coinbase has a simple and powerful mission, which is “to increase economic freedom in the world”.
How Coinbase makes money
Coinbase makes most of its money from transaction fees for services on its platform. In fact, transaction fees made up 90% of Coinbase’s revenue in 2020.
Below, there are some of the methods that Coinbase uses to make money:
Cryptocurrency to fiat conversion
Users who want to convert cryptocurrency to fiat are charged a margin or spread of up to 2% per transaction.
Transaction fees
Coinbase collects transaction fees from users for deposits, purchases, or crypto sales on the platform.
Buy and sale transactions
Coinbase charges a spread or margin on all, transactions such as buying and selling on its platform.
Coinbase debit card transaction fees
Coinbase offers a Coinbase debit card with a 2.49% transaction fee for purchases made with this card.
Selling digital assets
Coinbase also generates revenue from selling its own crypto assets.
Coinbase’s Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Coinbase Business Model Canvas below:
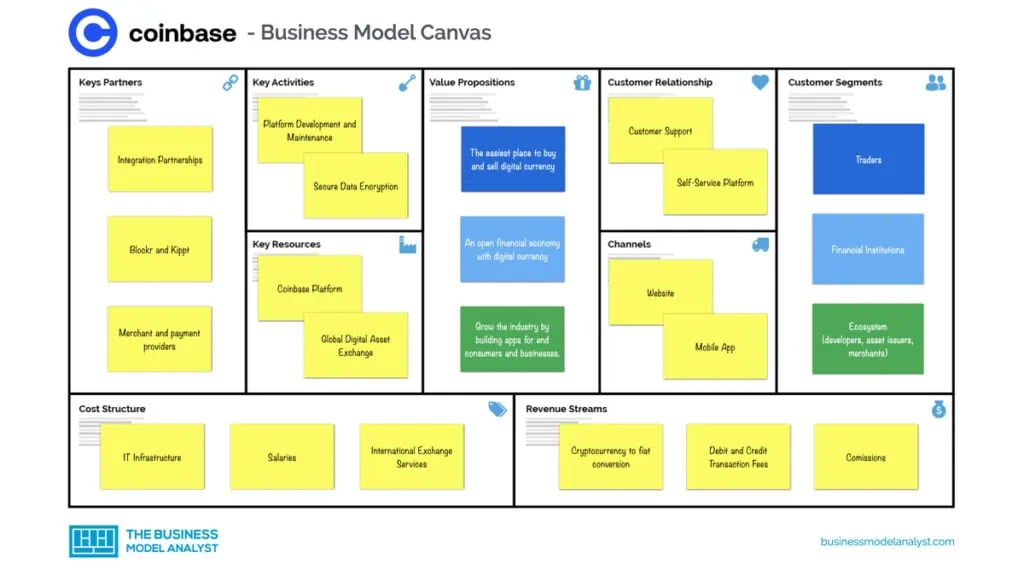
Coinbase’s Customer Segments
Coinbase’s customer segments consist of:
- Retail users: Coinbase has over 5 million monthly trading users (MTU);
- Institutions: Over 6000 institutions are using Coinbase;
- Ecosystem partners: Coinbase has over 100,000 partners which consist of developers, asset issuers, merchants, etc.
Coinbase’s Value Propositions
The Coinbase value propositions consist of:
- Creating an open financial economy with digital currency
- Be the easiest place to buy and sell digital currency
- Grow the industry by building apps for end consumers and businesses
Coinbase’s Channels
The Coinbase channels consist of:
- Websites
- Apps for Android and iOS
Coinbase’s Customer Relationships
The Coinbase customer relationships consist of:
- Customer service
- Support via e-mail and social media
- Self-service platform
- Community forum
Coinbase’s Revenue Streams
The Coinbase revenue streams consist of:
- Cryptocurrency to fiat conversion
- Transaction fees
- Commission
- Coinbase debit card transaction fees
- Credit transactions
Coinbase’s Key Resources
The Coinbase key resources consist of:
- Merchant and payment providers
- Coinbase platform
Coinbase’s Key Activities
The Coinbase key activities consist of:
- Currency conversion
- Payment processing
- Cryptocurrency exchange
- Wallet platform
- API software development
- NFT marketplace
Coinbase’s Key Partners
The Coinbase key partners consist of:
- Investors
- Buyers
- Sellers
- Asset Issuers
- Algo Traders and Other Developers
Coinbase’s Cost Structure
The Coinbase cost structure consists of:
- Platform development and maintenance.
- Datacenter operation.
- Payment of personnel.
- Rental of servers.
- International exchange services.
Coinbase’s Competitors
Below, there are some of Coinbase’s major competitors:
- Gemini: Gemini is a major rival to Coinbase which offers an all-in-one cryptocurrency exchange, wallet, and platform to buy, sell, and store digital assets;
- Binance: Founded in 2017, Binance is a cryptocurrency exchange platform with one of the highest Monthly Trading Volumes (MTU);
- Bittrex: Bittrex surpasses Coinbase in terms of the number of cryptocurrencies available. Bittrex has about 300 coins, compared to Coinbase with about 100 supported coins;
- Bitfinex: Owned by IFinex, Bitfinex is another cryptocurrency exchange platform that aims to create a superior trading experience;
- Robinhood: Robinhood is a financial technology company that offers a wide range of financial services. This platform offers various services for trading, investing, and storing currency;
- Kraken: Kraken was founded in 2011 as a cryptocurrency exchange and bank for currency and other digital assets.
Coinbase’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Coinbase:
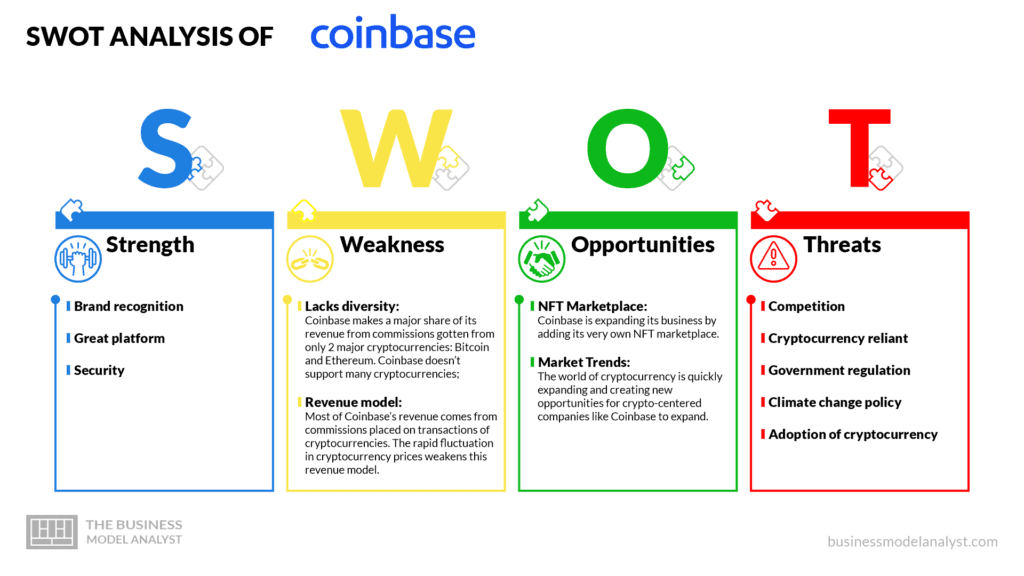
Coinbase’s Strengths
- Brand recognition: Coinbase is a widely recognized and trusted cryptocurrency exchange platform;
- Great platform: Coinbase offers its users a secure way to conveniently invest, trade, and store cryptocurrency;
- Security: The integration of standard banking security systems has made Coinbase a secure platform to store and exchange cryptocurrencies.
Coinbase’s Weaknesses
- Lacks diversity: Coinbase makes a major share of its revenue from commissions gotten from only 2 major cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin and Ethereum. Coinbase doesn’t support many cryptocurrencies;
- Revenue model: Most of Coinbase’s revenue comes from commissions placed on transactions of cryptocurrencies. The rapid fluctuation in cryptocurrency prices weakens this revenue model.
Coinbase’s Opportunities
- NFT Marketplace: Coinbase is expanding its business by adding its very own NFT marketplace.
- Market Trends: The world of cryptocurrency is quickly expanding and creating new opportunities for crypto-centered companies like Coinbase to expand.
Coinbase’s Threats
- Competition: Other cryptocurrency companies like Binance, FXT, and Kraken are quickly catching up to Coinbase. Another major competitor of Coinbase is Gemini, which also offers an NFT marketplace;
- Cryptocurrency reliant: The price of Coinbase’s stock relies heavily on the prices of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The volatile nature of cryptocurrency is a threat to Coinbase;
- Government regulation: Cryptocurrency exchange platforms are constantly facing regulations from the Government;
- Climate change policy: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Etherium face criticism for their negative impact on the climate. This leads to climate change policies that can threaten platforms like Coinbase;
- Adoption of cryptocurrency: Coinbase’s business model relies on the adoption of cryptocurrencies. This can make it harder for Coinbase to expand in some parts of the world.
Conclusion
Coinbase’s current business model is mainly focused on revenue generated from transaction fees, but this cryptocurrency-centered company is cooking up new updates to its platform and business model every year.
Coinbase is even planning for its very own NFT marketplace. So, how will Coinbase monetize this NFT marketplace, and what does it mean for its business model?
We’ll wait and see!

