Carvana is one of the most popular online used car retailers in the United States of America. Based in Tempe, Arizona, USA, Carvana buys, trades, and sells used cars to its customers throughout the United States. The Carvana Business Model works by sourcing cars from auctions, trade-ins, partnered dealerships, and individuals and selling them to customers at a higher rate than the original purchase to make a profit.
Carvana does not have physical showrooms; therefore, the whole buying and trading process takes place online, with customers having their cars delivered to their homes or picking them up at one of the 34 Carvana car vending machines scattered across the country.
Carvana has been a success since its inception. It is one of the youngest companies to be recently named to the 2021 Fortune 500 list, a list of 500 of the largest companies in the United States compiled annually by Fortune Magazine. Therefore, in this article, we will be examining the Carvana business model, its history, strengths, weaknesses, and everything that makes it a success.
Contents
A brief history of Carvana
Carvana was founded in 2012 by an American businessman, Ernest Garcia III, with Ryan Keeton and Ben Huston as co-founders. Garcia III joined his father’s company after he earned an engineering degree from Stanford University. His father’s company, DriveTime Automotive Group Inc., is an American-used car retailer and finance company formerly known as Ugly Duckling.
Garcia III started building Carvana in 2012 as a subsidiary of his father’s company, and bought most of Carvana’s used car inventory from DriveTime. Carvana got its initial funding round from DriveTime. The used car retailer and finance company also gave Carvana financial support, purchased its loans, and supplied it with technological assistance. However, DriveTime later spun off Carvana in November 2014, ending Carvana’s purchase of vehicles from DriveTime.
Carvana opened its first version of a car vending machine in November 2018. By 2016, Carvana opened a final, fully automated, coin-operated version of Carvana’s car vending machine in Nashville, Tennessee. Currently, Carvana has 34 car vending machines scattered throughout the United States. The tallest Carvana car vending machine stands nine stories tall and is located in Tempe, Arizona.
Carvana had its initial public offering and started trading on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol CVNA in April 2017. Carvana has since grown and acquired various companies to help improve the quality of its services. In 2017, Carvana acquired a rival automobile startup named Calypso to enhance its analytical tools and vehicle data.
Later in April 2018, Carvana acquired Car360, a startup known for its 3D computer vision, machine learning, and AR tech, with which it improves images of vehicles taken with a smartphone. Car360 was backed by Mark Cuban, an American billionaire entrepreneur, and was acquired by Carvana for $22 million.
During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Carvana introduced touchless delivery and pick-up, allowing customers to go through the entire car purchase process without direct contact with any employee. This move alone saw a 25% increase in vehicle sales and a 13% increase in gross revenue. Carvana became the second-largest online used-car retailer in the U.S. in 2020 after selling 244,111 vehicles and recording an annual revenue of $5.587 billion.
Who Owns Carvana
Carvana is owned by 65.15% of institutional shareholders and 57.48% of Carvana co-insiders. Ernest Garcia II, the father of Carvana’s founder, is the largest individual Carvana co-shareholder. He owns 45.18% of the company, representing 82.5M of Carvana’s total shares. His shares are currently valued at $1.46B. Garcia III, the founder, and CEO of Carvana, owns $600 million of Carvana stock. Due to their super-voting shares, Garcia III and his father have complete control.
Other top shareholders of the company include Price T. Rowe Associates Inc. (10.65%), Baillie Gifford Co (5.78%), Vanguard Group Inc. (4.71%), Cas Investment Partners LLC (3.57%), Spruce House Investment Management (3.26%), and Fmr LLC (3.00%). Other shareholders include Spruce House Partnership Ai LP, Morgan Stanley, and Blackrock Inc.
Carvana is headed by its founder and Chief Executive Officer, Ernest Garcia III, with co-founder Ryan Keeton as the Chief Brand Officer and co-founder Ben Huston as the Chief Operating Officer.
Carvana’s Mission Statement
“To change the way people buy cars by providing our customers a car-buying solution that is fun, fast, fair, and powered by technology.”
How Carvana makes money
Carvana operates a retail business model. This type of business model involves the sale of a finished product directly to the final consumers. In Carvana’s case, the finished products are the cars that are sold to people in need of them. To make a profit, Carvana sources cars from various channels and sells them to customers at a rate higher than the original purchase.
Used Car Retail Sales
The revenue generated from retail car sales constitutes Carvana’s primary source of revenue. In 2021, Carvana made $9.9 billion from retail car sales, accounting for 77.3% of the company’s total revenue. Carvana adds the cost of marketing, inspection, maintenance, and transportation of their vehicles to the purchase cost.
The cost difference between these expenses and the vehicle’s selling price is how Carvana makes a profit. To purchase cars from Carvana as a retail buyer, customers use the Carvana app or website to search for their preferred cars.
With Carvana’s 360° photo technology, customers can inspect their preferred car and even take it on a virtual spin. If the car is not available for purchase, customers can set alerts to notify them if the vehicle becomes available. If the vehicle is available, customers can view the total price, which covers taxes, title, and registration.
Wholesale Car Sales
Although Carvana operates as a used car retailer, it also sells wholesale to traditional auto dealers, which is its second-largest source of revenue. Carvana carries out a thorough inspection of all vehicles before they are put up for sale. Excess stock and vehicles that do not pass Carvana’s strict inspection are sold to other dealerships.
In 2021, Carvana made $1.9 billion from wholesale car sales alone. Wholesale dealers willing to buy vehicles that did not pass Carvana’s inspection test can do so through CarvanaACCESS, Carvana’s direct purchase platform for wholesale buyers. Carvana gets a higher profit margin on wholesale deals because it does not have to spend much on inspection and maintenance for these lower-quality vehicles.
Financing
Another reason for Carvana’s increasing popularity is its willingness to sell cars to people who need them but cannot afford them at the moment. Carvana offers three different payment options to its customers. The first option is to pay with cash. However, people who cannot afford to pay with cash can either get one of Carvana’s auto loans or take a third-party loan.
Carvana can help its customers get qualified for an auto loan through an online process that does not require tedious paperwork. Customers can get suitable loans for as long as 45 days without any impact on their credit scores. This auto loan option is another way Carvana provides value for its customers, who do not have to go through the long process of securing loans from third-party companies. The interest rates on these loans serve as another revenue stream for Carvana.
Vehicle Service Protection
Carvana offers a variety of coverage for its customers’ vehicles. Every vehicle sold by Carvana comes with a 100-Day or 4,189-mile limited warranty. Carvana’s limited warranty only covers repairs on most mechanical and electrical failed vehicle components such as engine, transmission, suspension, A/C & heating, steering, etc. The warranty also covers roadside assistance; however, these benefits only last for 100 days or 4,189 miles after purchase. Under the Carvana limited warranty, any covered repair carried out at a preferred repair facility comes at no extra cost to the customer. However, a covered repair at a non-preferred facility can cost as much as $200.
For customers who want more than the benefits of a limited warranty, Carvana offers various vehicle service protection contracts (VSC). Carvana’s VSC covers the rest of the damages, which are not covered by the limited warranty. There are different Carvana vehicle service protection packages that customers can choose from. It allows them to choose how much coverage they want for their vehicle systems.
Carvana’s VSC is not limited and does not expire after a set number of days or mileage. Customers continue to enjoy vehicle service protection as long as they pay for it. Sometimes, customers can transfer the vehicle service protection contract from one user to another. This feature adds to a vehicle’s resale value if a Carvana customer decides to sell their car.
Insurance
Insurance is a requirement to drive in every state in the United States of America. Therefore, Carvana helps to simplify the process of getting insurance for its customers. Through Root Insurance Co., Carvana makes insurance available to its eligible customers who purchase vehicles. Root Insurance Co. is a digital insurer, in which Carvana previously invested $126 million to provide insurance for its customers. Insurance is another way through which Carvana makes money.
Carvana also offers GAP coverage to its financing customers. Guaranteed auto protection, also known as GAP insurance, is a type of insurance that is only needed for a short period while the value of a loan taken to buy a car is greater than the value of the car. GAP insurance works such that if a Carvana customer’s car gets totaled in an accident or stolen, the Guaranteed Auto Protection covers the gap between the depreciated value of the car and the amount owed on the loan. GAP coverage is optional but advisable since standard car insurance does not give this extra layer of protection.
Carvana’s Business Model Canvas
The Carvana Business Model can be explained with the business model canvas below:
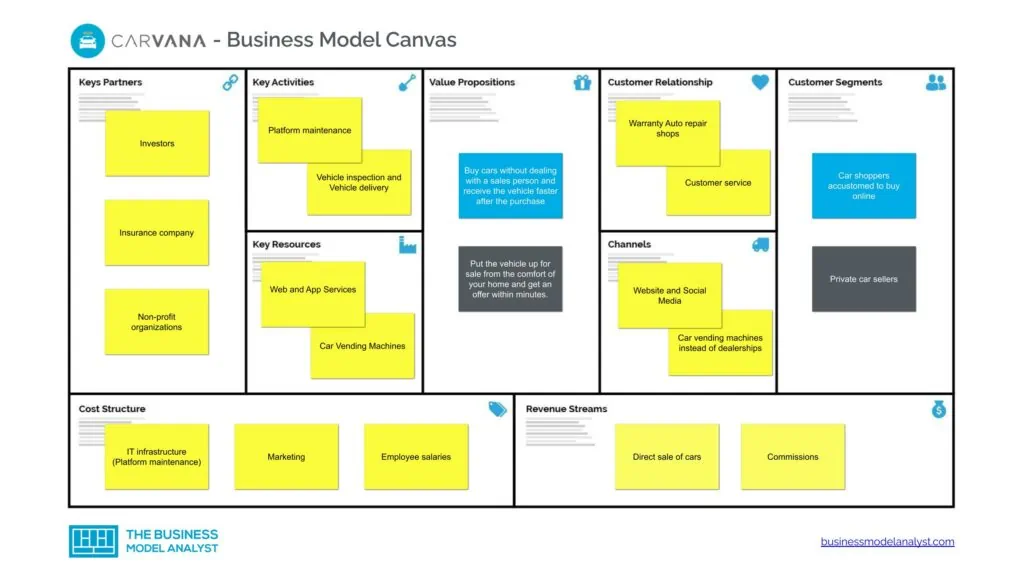
Carvana’s Customer Segments
Carvana operates only in the United States, therefore, its services are limited to the people there. Carvana’s customer segment consists of the following:
- Buyers: The buyers of Carvana are the people who purchase vehicles from the company. Two types of buyers make up Carvana’s customer segment. These are retail buyers and wholesale buyers. Retail buyers are customers that purchase vehicles in units primarily for personal use. Retail buyers are a significant component of Carvana’s customer segment because they are the company’s primary source of revenue. Retail buyers access the Carvana app or website to purchase cars on Carvana. The purchased car is delivered directly to the customer’s home or a local Carvana market for pickup. Wholesale buyers, on the other hand, are people that purchase vehicles in bulk. Wholesale buyers help to take excess stock or cars that do not pass inspection off Carvana’s hands. Wholesale buyers do not purchase vehicles through the same channel as retail buyers. They must purchase through CarvanaACCESS, Carvana’s direct platform for wholesale buyers;
- Sellers: While Carvana mostly gets its inventory from auctions and partnered dealerships, it also purchases some of its cars from individuals who sell them. Cars purchased by Carvana undergo rigorous inspections to ensure they meet all of Carvana’s high standards. Therefore, sellers are another significant part of Carvana’s customer segment. Since Carvana sells used cars and does not produce cars, it relies on its sellers for its inventory.
To sell a car on Carvana, sellers need to access the sell/trade page on the Carvana website. To get an offer for their vehicles, sellers must share details like their car’s VIN and answer a few questions. Carvana sends a genuine offer within minutes of the sellers sharing a few necessary details. Carvana presents its sellers with the best offers based on the condition and details of their vehicles and the market condition. If sellers agree to Carvana’s offer, they can get paid in no time by check or direct deposit. Sellers can then drop off the old car at the nearest vending machine or schedule a pickup;
- Trade-in Dealers: Trade-in dealers are buyers and sellers at the same time. A trade-in at Carvana involves the purchase of a car the customer is interested in and the sale of the car currently owned by the customer at the same time. The first step to initiate a trade-in at Carvana is selling the existing car. Similar to the sale of a car to Carvana, customers have to access the sell/trade page on the Carvana website or app. After answering a few questions, Carvana presents an offer valid for seven days, giving customers time to browse for their preferred new car. The value of the offer on the existing car is subtracted from the sale price of the car the customer intends to purchase. Also, in some states, customers can be eligible for state tax savings, which allows them only to pay tax on the difference between the price of the new car and the traded existing car.
Carvana’s Value Propositions
To keep its customers, Carvana provides value for every member of its customer segment. Carvana’s value propositions consist of:
Value Propositions to Buyers
Carvana’s buyers make up a very significant part of Carvana’s customer segment. Therefore, to retain them, Carvana offers services that create value.
The following are Carvana’s value propositions for its buyers:
- Ease and Comfort: Carvana is changing the car dealership game. It offers a lot of advantages for its customers over traditional dealerships. With Carvana, buyers do not have to leave the comfort of their homes to purchase a vehicle. The entire process can be carried out on a mobile phone with an internet connection. Buyers do not even have to leave their homes to get their vehicles;
- Price Transparency: From the comfort of their homes, buyers on the Carvana platform can easily compare the prices of different vehicles sold by Carvana based on characteristics such as mileage, brands, etc. Buyers get the best prices depending on the condition of the vehicle. This service helps buyers to escape haggling to beat down prices and the stress of dealing with pushy salespeople;
- Financing: Carvana makes provisions for customers willing to buy vehicles but cannot afford them at that particular time. Carvana provides easy auto loans for its customers in need of it. Buyers can secure easy loans in a short time with no impact on their credit score via the Carvana platform. These loans can be used to purchase any vehicle of choice from Carvana;
- Return Policy: Before purchasing a vehicle, buyers can inspect their preferred cars and even take them on a virtual spin using Carvana’s 360° technology. This technology gives buyers enough time to decide if they like the vehicle before purchasing. It also ensures that the buyer has complete knowledge of the vehicle they are about to buy. Nevertheless, Carvana’s 7-day return policy allows buyers to return the vehicle after purchase if unsatisfied. This policy ensures that buyers can test their cars physically to decide if they like them, giving them total value for their money;
- Referral Bonus: For every new buyer that an existing customer refers to Carvana, both the new buyer and the existing customer are eligible for referral gifts. The new buyer must keep the purchased vehicle past the 7-day return window for both parties to receive the gifts. Due to state restrictions, the kind of gifts received might vary. However, some common gifts include Apple AirPods, traveling bags, vacuum cleaners, handheld espresso machines, etc. In other instances, the existing customer is eligible to receive a $100 check, while the newly-referred buyer gets $500 off their purchased vehicle;
- Delivery: Unlike most traditional dealerships, buyers do not need to go to the car dealerships to get their purchased vehicles. Carvana delivers purchased cars to their customers on schedule. Buyers can also visit the nearest Carvana car vending machine to pick up their vehicles;
- Warranty: Every vehicle sold by Carvana comes with a 100-day or 4,189-mile limited warranty. This warranty covers repairs on mechanical and electrical failed vehicle components such as transmission, suspension, engine, steering, A/C & heating, etc.
After purchasing a car, buyers can get a free repair from Carvana if their car develops any warranty-covered damage within 4,189 miles of coverage or 100 days after purchase. Buyers can also buy any of Carvana’s vehicle service protection contracts for damages that are not covered under the limited warranty. While the limited 100-day warranty is free, buyers must pay for an extended warranty plan that covers more than basic repairs. There are three extended warranty plans: CarvanaCare Essential, CarvanaCare Plus, and CarvanaCare Premium.
- CarvanaCare Essential: This extended warranty plan covers the repairs of a vehicle’s powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.) alongside other basic repairs;
- CarvanaCare Plus: This covers the mechanical and electrical components of a vehicle;
- CarvanaCare Premium: This combines the benefits of the Essential and Plus plans. Buyers subscribed to this service are eligible for free engine oil and tire changes for one year. They also enjoy the repair of minor dents or scratches to some body parts of the vehicle.
This value propositions to the buyers give them a sense of security when purchasing from Carvana.
Value Propositions to Sellers
Since Carvana does not produce cars, it gets its inventory from its sellers. The following are Carvana’s value propositions for its sellers:
- Ease and Comfort: Carvana has eliminated the need to visit a dealership or negotiate private sales before selling a vehicle. Sellers can now put their vehicles up for sale from the comfort of their homes and get a genuine offer from Carvana within minutes;
- Best Prices: Customers do not need to go through the stress of haggling because Carvana offers the best prices based on the vehicle details and the reigning market conditions. Getting the best prices on offers saves a seller a lot of time and energy that would have been spent negotiating;
- Fast and Secure Payment: Carvana offers fast and secure payments to its customers through checks and direct deposits;
- Flexible scheduling for Pickup or Dropoff: After finalizing a vehicle sale, the seller can schedule a time and place for Carvana to pick the vehicle up. Also, a seller can drop the sold vehicle off at the nearest Carvana hub or vending machine. These ensure the safety of sellers;
- Offer Duration: Purchase offers from Carvana last for seven days. This duration is less than the industry’s average, and it can result in higher selling prices.
Carvana’s Channels
Carvana’s channels consist of:
- Website: Carvana’s major channel of distribution is its website. Buyers, trade-in dealers, and sellers all have to access the Carvana website to buy, trade in, or sell their vehicles. Other features such as financing and insurance can all be accessed through the Carvana website;
- Mobile Apps: Carvana has a mobile application designed to function on both the Android and iOS operating systems. The app provides easy access to all of Carvana’s features. Carvana’s customers can download the app from the Google Play Store for Android devices and the Apple App Store for iOS devices.
Carvana’s Customer Relationships
Carvana’s customer relationships consist of:
- Carvana Car vending machine
- Customer service
- Social media platforms
- Referral bonus
- Warranty Auto repair shops
Carvana’s Revenue Streams
Carvana’s revenue streams consist of:
- Car Sales: Carvana is a used car retailing company; therefore, its primary source of revenue is the profit made on the sale of its vehicles. Carvana purchases its cars from customers who trade their cars in or sell them, auctions, and partnered dealerships. These cars are then sold at a rate higher than the original purchase. The difference between the purchase price and the selling price is what constitutes Carvana’s profit.
Although Carvana is majorly a retailing company, it also makes wholesale car sales on excess stock and cars that do not pass its rigorous inspection. In 2020, Carvana sold about 244,111 used cars and made $4.7 billion, which equals 84.2% of its total income;
- Sales from other sources: Carvana provides some other services, apart from the sales of cars, which help it to generate more revenue. Other services that constitute an additional source of revenue for Carvana are the sale of automobile financing, Vehicle service contracts’ (VSC) sales commissions, and GAP waiving sales, according to the company’s Form 10-K in 2020. The company also makes money from interest on loans and by selling extended warranty plans that cover maintenance services that are not already covered by the manufacturer’s warranty.
Carvana’s Key Resources
Carvana’s key resources consist of:
- Web and App Services: This refers to Carvana’s websites and mobile applications available for various devices, through which buyers and sellers interact with Carvana;
- Active Buyers and Sellers: Carvana cannot exist without its customer segment. Therefore, buyers and sellers on the Carvana platform are a part of Carvana’s key resources;
- Car Vending Machines: Carvana’s car vending machines scattered around the country are a part of its physical key resources;
- Used Cars: The vehicles that Carvana buys and sells are important key resources that determine the success of its business model;
- Human Resources: This refers to the Carvana employees who are responsible for the maintenance of its platform and car vending machines, pickup and dropoff of sold and bought vehicles, and those who work in Carvana’s auto-service shops. Carvana had 21,000 employees as of December 2021.
Carvana’s Key Activities
Carvana’s key activities consist of:
- Platform maintenance (websites and mobile apps)
- Vehicle inspection
- Customer service
- Product Marketing
- Car Vending machine maintenance
- Delivery and Pickup
Carvana’s Key Partners
Partnerships result in mutual benefits for the parties involved. Carvana’s key partners include:
- Investors
- Insurance company (Root Insurance Co.)
- Non-profit organizations (Carpool charity fund, Arizona animal shelter, etc.)
- Buyers
- Sellers
- Suppliers
- Marketing agencies
Carvana’s Cost Structure
Carvana incurs various types of costs. Carvana’s cost structure includes:
- Physical structures and facilities (Car vending machines and hubs, auto service shops, etc)
- Platform maintenance (websites and mobile applications)
- Inventory expenses
- Employee salaries
- Inspection of vehicles
- Maintenance of vehicles
- Referral bonuses and gifts
- Logistics and storage expenses
- Administrative costs
- Marketing
Carvana’s Competitors
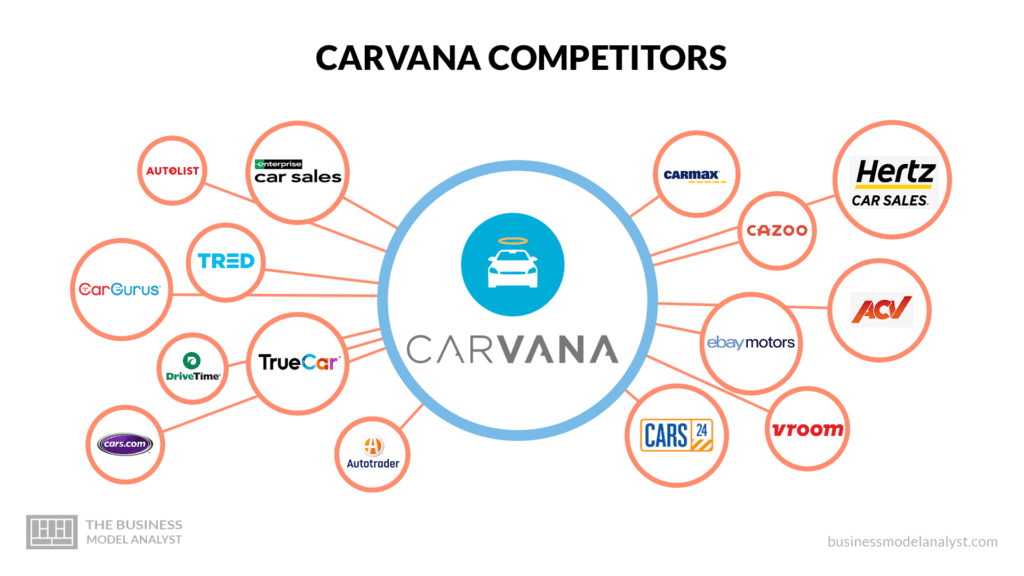
Despite being one of the most popular online used car retailers in the United States of America, Carvana is not without its competitors. Carvana’s competitors include:
- CarGurus: CarGurus is an online automotive research and shopping platform that is seen as one of Carvana’s top competitors. Founded in 2006, CarGurus is located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. CarGurus was founded seven years before Carvana. Unlike Carvana, CarGurus does not have a physical inventory. None of the cars listed on CarGurus’ platform belongs to the company. It connects sellers with potential buyers. While Carvana deals only in used cars, CarGurus deals in both new and used cars. On CarGurus, potential buyers can compare local listings before contacting a seller to purchase a vehicle. CarGurus provides a way for people to shop for new and used cars from different places. Like Carvana, the company also provides auto loans to its customers;
- Vroom: Founded in 2013, Vroom is an online marketplace on which people can buy, sell, and trade-in used cars. Vroom has its headquarters in New York City and provides similar services to Carvana, making it a major competitor. Vroom allows customers to search for vehicles by make, model, year, and location. Customers can also inspect the car through photos, and view the car’s specs, and pricing information. Like Carvana, Vroom offers auto financing to its customers. However, Vroom has a more flexible pricing model than Carvana. Buyers are not pressured and do not need to haggle;
- CarMax: CarMax is an auto dealership founded in 1993. Its headquarters is located in Richmond, Virginia. CarMax is one of Carvana’s competitors. CarMax specializes in new and used cars and, like Carvana, it allows users to browse listings for a vehicle of their choice. CarMax offers affordable prices to its customers and provides easy financing that allows them to pay an affordable sum of money every month after down payment. CarMax allows its customers to take vehicles on a 24-hour test drive. Unlike Carvana’s 7-day return policy, CarMax offers a 30-day return policy after purchase;
- Cars.com: Cars.com is a leading automotive marketplace founded in 1998 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Cars.com serves about 26 million car buyers and sellers on its website and mobile application per month. On its website, Cars.com updates its inventory of over 50,000 cars every day. In addition to posting vehicles for sale, Cars.com offers editorial content and millions of reviews. Cars.com is one of Carvana’s biggest competitors;
- Auto Trader Group: Autotrader is an online marketplace for buyers and sellers of new and used cars. It was founded in 1997 and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. Autotrader certifies used cars and puts them up on its platform for sale. In addition to selling cars, Autotrader provides its users with automotive reviews, shopping advice, and tools for comparing car financing and insurance information.
Carvana’s SWOT Analysis
The following is a well-detailed SWOT analysis of the Carvana business model:
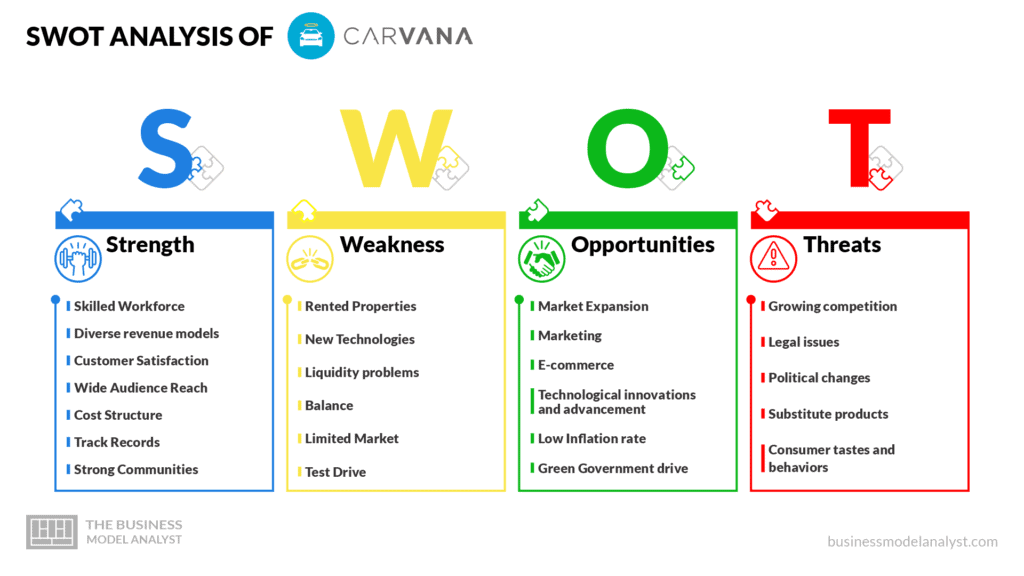
Carvana’s Strengths
- Skilled Workforce: Carvana has invested huge resources in training and learning programs for its employees. Therefore, it is no surprise that it has a large number of highly trained and talented employees working in the company. A highly-skilled workforce ensures the growth and development of the company;
- Diverse revenue models: Although the major source of revenue for Carvana is the sale of cars, it has been able to create value through other services. These services serve as extra sources of revenue for the company;
- Customer Satisfaction: Carvana has a strong relationship with its customers, and this has helped it to achieve a high level of customer satisfaction among its existing customers. This strengthens the brand’s recognition and encourages potential customers;
- Wide Audience Reach: Carvana ensures that its services are easily accessible to its customers. There are Carvana hubs scattered all over the country and vehicles can be delivered to a customer anywhere in the United States;
- Cost Structure: Carvana has made its goods affordable for all and sundry. People who cannot afford to pay right away for a vehicle can choose from Carvana’s easy financing options;
- Track Records: Carvana has a successful track record of product innovation and integration of useful technology by merger or acquisition. Carvana always strives to improve the quality of the services provided to its customers;
- Strong Communities: Carvana has built a strong connection with its dealers and distributors. This encourages the dealers and distributors to promote Carvana’s products.
Carvana’s Weaknesses
- Rented Properties: Carvana has a lot of physical structures and facilities, however, most of them are rented out. Since rent is recurring, it increases the company’s expenses
- New Technologies: Carvana needs to invest in new technologies to make its expansion and venture into newer geographical locations easier;
- Liquidity problems: As a result of improper financial planning, Carvana lacks current assets relative to current liabilities. Therefore, this can lead to liquidity problems in the future;
- Balance: While Carvana spends a lot of money on research and development, it does not invest well in profitable things like other industry players;
- Limited Market: Carvana only operates in the United States, therefore, its services are limited to the country. This also limits the company’s revenue stream and growth capabilities;
- Test Drive: Unlike some of its competitors, Carvana does not allow customers to test drive a car physically before purchase. Customers may take a car for a virtual spin with the help of Carvana’s 360° photo technology. Also, they can choose to return their vehicle within 7 days of purchase. However, they are not allowed to test drive their chosen vehicle before purchase. This may lead to some customers going for Carvana’s competitors.
Carvana’s Opportunities
- Market Expansion: Carvana can expand, try new geographical locations, and enter new international markets. This will contribute to the growth and development of the company and help to generate more revenue;
- Marketing: Carvana can take advantage of social media platforms to market its goods, interact with its customers, and build solid relationships with them. A solid online presence for Carvana ensures that its goods and services reach a wider audience;
- E-commerce: Since the COVID-19 pandemic, more people have been purchasing goods and services via the internet. Carvana can take advantage of this wave of development and create online storefronts for its products;
- Technological innovations and advancement: Advancements in technology can help Carvana test out new products and markets. Technological innovations can also aid the automation of several operations, thereby reducing costs;
- Low Inflation rate: Low inflation rate makes the market stable. This affords Carvana the opportunity of reducing its costs of inputs;
- Green Government drive: This refers to the activities of the government to increase the use of renewable energy. This opens up an opportunity for Carvana to sell its products to federal and state government contractors.
Carvana’s Threats
- Growing competition: Carvana has a very simple business model that is easy to imitate. Although Carvana is one of the first movers in the car retailing industry, there are hundreds of car retailing companies in the market now that provide the exact services as Carvana;
- Legal issues: Carvana is known to get into legal trouble from time to time. Sometimes, its business license gets suspended, or business activities get banned. This threatens the existence of the company;
- Political changes: Change in laws can cause market instability and revenue loss. This can also incur unnecessary expenses for the company;
- Substitute products: Substitute products are fast being released. This decreases the purchase and consumption of the current products, thereby threatening the entire industry;
- Consumer tastes and behaviors: Constant changes in customers’ tastes and behaviors pressures companies to change their products to cater to the needs of their customers.
Conclusion
Carvana operates a retail business model that has grown to become one of the most popular in the United States, despite facing fierce competition. Carvana operates only in the United States, however, there are a lot of opportunities that can be tapped from new markets. Carvana provides a platform on which people can buy and sell used cars without having to go through long hours of negotiation and haggling that is experienced in traditional dealerships.

