The Canva business model is a SaaS that provides graphic design software for people who are not professional designers and don’t have an interest or cannot afford to hire one. The user has access to innumerable ready-made templates, fonts, and even free images, in a user-friendly interface, able to feed any kind of social media, and more. Keep reading to understand how this company which started from two in-love Australian youngsters back in 2012 became a graphic design software used by 85% of Fortune 500 companies.
Contents
A brief history of Canva
Despite the foundation, in 2012, Canva’s journey began five years before, when Melanie Perkins and Cliff Obrecht were students at the University of Western Australia. At that time, Perkins used to give InDesign and Photoshop classes to students — and realized that people considered that software really tricky to learn and use, indeed. The students would append nearly half a year only learning what the available tools in the applications were, and Perkins thought there should be a way of doing the same kind of work with simpler tools. This way, together with her boyfriend, Obrecht, Perkins had the idea of developing a simple online tool to create school yearbooks.
They took a loan and built Fusion Books. Users would design the books, while the young couple would print and deliver them to schools across Australia. It was a success — and remains: It is currently the largest school yearbook publisher in the country, with expansion in New Zealand and France. But, as Canva can tell now, they have not stopped there. Some years later, in 2010, Perkins attended a conference in Perth and met Bill Tai, a legendary venture capitalist from Silicon Valley.
Tai was a passionate kitesurfer and Perkins realized that practicing the sport would be a way to keep in contact with the investor, and, thus, have a network. Her dedication paid off, and, in a short time, they won major investments and were able to create Canva with a great team of engineers. But, to go beyond that, they would need some tech person, and that came with Cameron Adams, one ex-Google.
A few months after that, in 2012, their first funding round was able to put the Canva website online. Nowadays, Canva has helped create around 2 billion designs in 190 countries. Its valuation reached USD 15 billion in 2021 and keeps counting.

Who Owns Canva
Founded in 2013, Canva is still owned by its founders, with Melanie Perkins as the company’s CEO.
Canva’s Mission Statement
Canva’s mission statement is “To empower everyone in the world to design anything and publish anywhere“.
How Canva makes money

Canva is a freemium business model: It is free to use, with subscription plans that offer additional features, images, and templates. There are five revenue streams at Canva:
1. Canva Pro
Canva Pro is a premium subscription plan, with prices starting at $6.50 per month, depending on how many users will use the subscription. The Pro features include:
- 75+ million premium stock photos, videos, audio, and graphics
- 420,000+ free templates with new designs daily
- 1 Brand Kit with your own fonts and logos
- Unlimited use of Background Remover
- Saving designs as templates for your team to use
- 100 GB of cloud storage
- Scheduling social media content to 7 platforms

2. Canva Enterprise
Canva Enterprise is another subscription plan, aimed at large businesses, interested in managing their brand. The cost starts at $20.50 per person, monthly. The Enterprise features include:
- Establishing your brand’s visual identity with logos, colors, and fonts across multiple Brand Kits
- Controlling your team’s access to apps, graphics, colors, logos, and fonts with brand controls
- Controlling team uploads into Canva
- Built-in workflows to get approval on your designs
- Setting which elements your team can edit, and stay on-brand with template locking
- Unlimited storage
- Single-sign on (SSO)
- 24/7 Enterprise-level support
Educations institutions have discounts on the Enterprise plan, and non-profit organizations can access it at no cost.
3. Canva Print
Canva has partnered with printers to print and deliver the material printed. Users can make their designs in the applications and receive the physical material at their address. Canva charges the service according to the type of product, order volume, and location for delivery.
4. Marketplace
Sometimes people do not see the necessity of subscribing but want to buy some premium design. In these cases, Canva charges a one-time fee for single usage. Users can find paid images and templates, ready to use. The content is developed by designers, who leave their work available on the platform. For every sale, Canva takes 35%. For content sold in the Pro plan, creators received 50% (cutting off taxes and processing fees).
5. Design School
Canva also has a Design School, by which the company offers online and in-person classes, about design, branding, and social media, hosted by Canva’s experts. Online classes are free and the presential ones start from $5.

Canva’s Business Model Canvas
The Canva Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
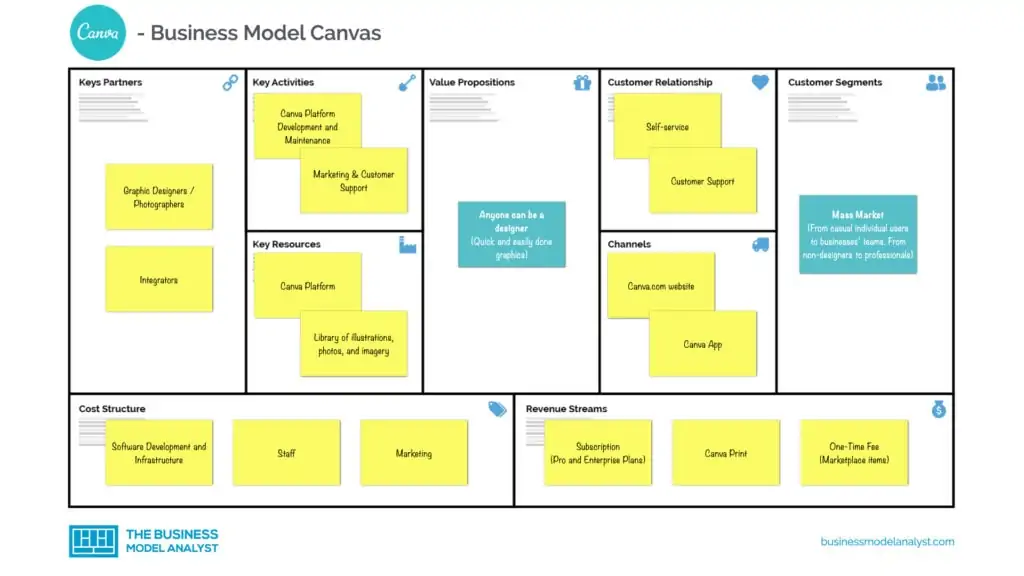
Canva’s Customer Segments
Canva’s customer segments consist of:
- Anyone, from casual individual users to business teams
- From non-designers to professionals
- From non-profit organizations to educational institutions
Canva’s Value Propositions
Canva’s value propositions consist of:
- Simple and flexible design platform
- Quick and easily done graphics
- Marketing material with no expertise
- Variety of customization
- Accessible through mobile and browsers
Canva’s Channels
Canva’s channels consist of:
- Website
- Mobile app
- Canva button (integrated into any website that hosts user-designed content)
- API
- Social media
- Affiliate program
Canva’s Customer Relationships
Canva’s customer relationships consist of:
Mostly self-service, but the platform offers the marketplace, the Design School, a blog, and social media accounts.
Canva’s Revenue Streams
Canva’s revenue streams consist of:
Canva’s revenue is based on the sale of user subscriptions and single-use licensing of content. Additionally, there are the Design School in-person classes and printed delivered material.
Canva’s Key Resources
Canva’s key resources consist of:
- Graphic design platform
- IT infrastructure
- Library of illustrations, photos, and imagery
- Staff
- Design community
- Contributor partners
Canva’s Key Activities
Canva’s key activities consist of:
- Graphic design
- Platform maintenance
- Product development
- Marketing and sales
- SEO
- Operation
- Support
- Integrations
Canva’s Key Partners
Canva’s key partners consist of:
- Graphics contributors
- Integrators
- Marketers
- Third-party apps and websites
- Investors
- Bloggers
- Affiliates
Canva’s Cost Structure
Canva’s cost structure consists of:
- Software development
- Infrastructure maintenance
- Network
- Personnel
- Marketing and affiliates
- Administration
Canva’s Competitors
- Lucidpress: Developed by Lucid Software, it is a web-based app that allows the user to create brochures, flyers, newsletters, business cards, posters, magazines, and presentations. It has both free and paid subscriptions;
- Venngage: Also with both free and paid subscriptions, Venngage is a Canadian web-based software, especially focused on infographic creation;
- Fotor: Launched in 2012, it is a very complete photo-editing app, downloadable on both Android and iOS platforms, as well as on Windows and macOS operating systems;
- Prezi: Founded in 2009 and based in Budapest, Hungary, Prezi is a visual communications software company, which is specialized in presentations;
- Adobe InDesign: Focused on the creation of posters, flyers, brochures, magazines, newspapers, presentations, books, and e-books, Adobe InDesign is one of the most famous tools of Creative Cloud, which needs a paid subscription to be properly used after its trial;
- Adobe Lightroom: Another Adobe product, Photoshop Lightroom is a full-scale free image manipulation software. Different from other Adobe products — such as Photoshop itself, the original one —, it can be downloaded not only on desktop but also on mobile, with its Android/iOS app;
- GIMP: One of the internet dinosaurs, GIMP was launched in 1998 and evolved its resources and features throughout the years. It is, to this day, a very complete photo-editing tool, with an app for iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS.
Canva’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Canva:
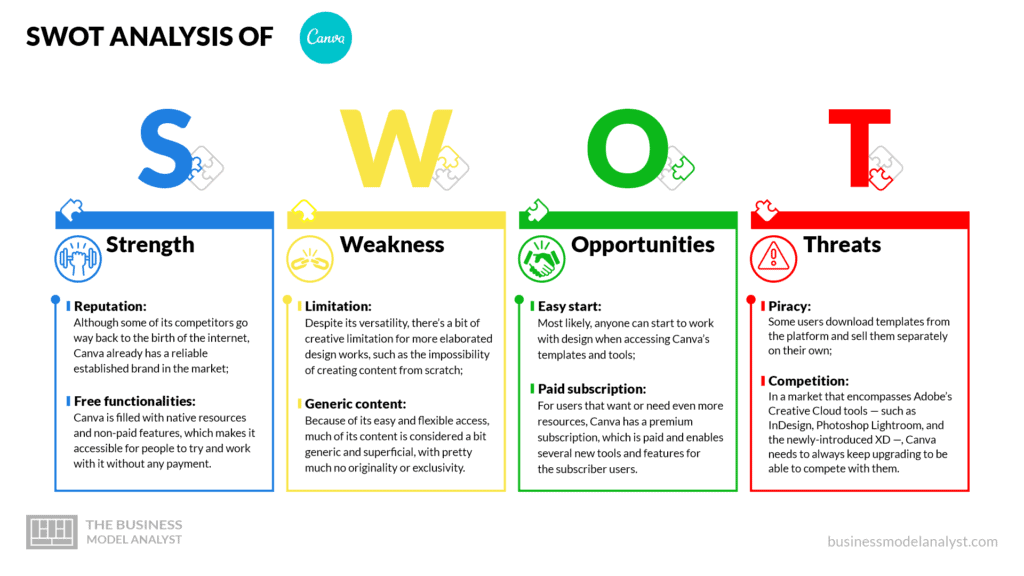
Canva’s Strengths
- Reputation: Although some of its competitors go way back to the birth of the internet, Canva already has a reliable established brand in the market;
- Free functionalities: Canva is filled with native resources and non-paid features, which makes it accessible for people to try and work with it without any payment.
Canva’s Weaknesses
- Limitation: Despite its versatility, there’s a bit of creative limitation for more elaborated design works, such as the impossibility of creating content from scratch;
- Generic content: Because of its easy and flexible access, much of its content is considered a bit generic and superficial, with pretty much no originality or exclusivity.
Canva’s Opportunities
- Easy start: Most likely, anyone can start to work with design when accessing Canva’s templates and tools;
- Paid subscription: For users that want or need even more resources, Canva has a premium subscription, which is paid and enables several new tools and features for the subscriber users.
Canva’s Threats
- Piracy: Some users download templates from the platform and sell them separately on their own;
- Competition: In a market that encompasses Adobe’s Creative Cloud tools — such as InDesign, Photoshop Lightroom, and the newly-introduced XD —, Canva needs to always keep upgrading to be able to compete with them.
Conclusion
After the acquisitions of Zeetings in 2018, Pixabay and Pexels in 2019, and Kaleido.ai and Smartmockups in 2021, Canva now seems to be on the rise and has relatively significant domination of the market.

