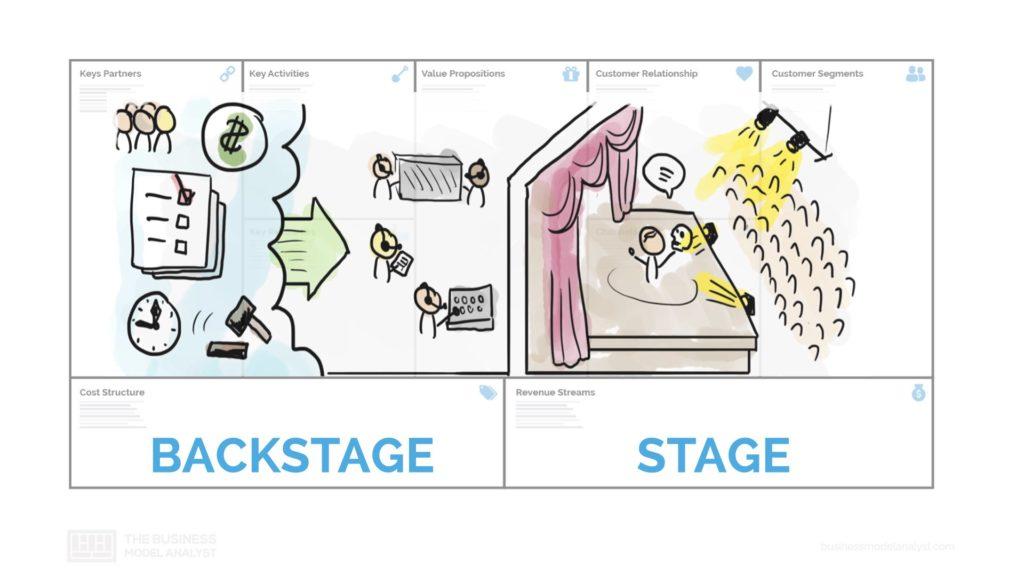
The term business model has gained incredible popularity in the last decade as one of the most important ways of approaching business innovation and business strategy. If you’re like most people, you probably define business model as a company’s plan for making money. And you’re not the only one. Probably 80 to 90% of people think like that. This article will show you that the business model is not just that. It is much more. The term is still relatively new and still raises a lot of doubts about its definition and how it works. In fact, an efficient business model is much more comprehensive and deeper than how a company charges its customers. It involves identifying customer segments, delivery channels, key-partners, among other things. It is much more than simply establishing how a company makes money. It’s about explaining how it can create and deliver value to consumers. Part of a business model includes the activities associated with production: design, supplies, raw materials, manufacturing (backstage). But there is a second part that involves other essential activities when selling a product: finding your audience, closing a sale, distributing a product, delivering a service (stage). This is known as the two sides of a Business Model. The customer-facing part is the stage and the behind-the-curtains part is the backstage. Most of the time, we only see strategies of what’s “visible” to us, but there are many innovations that happen and we don’t notice.
Check out our super guide about business models sides with 6 mental models explained to help you interpret and design business model strategies:

Check it out by clicking here. The essence of a business model is that it defines the manner by which the business enterprise delivers value to customers, entices customers to pay for value, and converts those payments to profit: it thus reflects management’s hypothesis about what customers want, how they want it, and how an enterprise can organize to best meet those needs, get paid for doing so, and make a profit. Any business, therefore, depends on a well-designed and thoughtful business model, which covers all these aspects, so that this company is set on a strong base. So let’s start with the basics.
Contents
What is a business model?
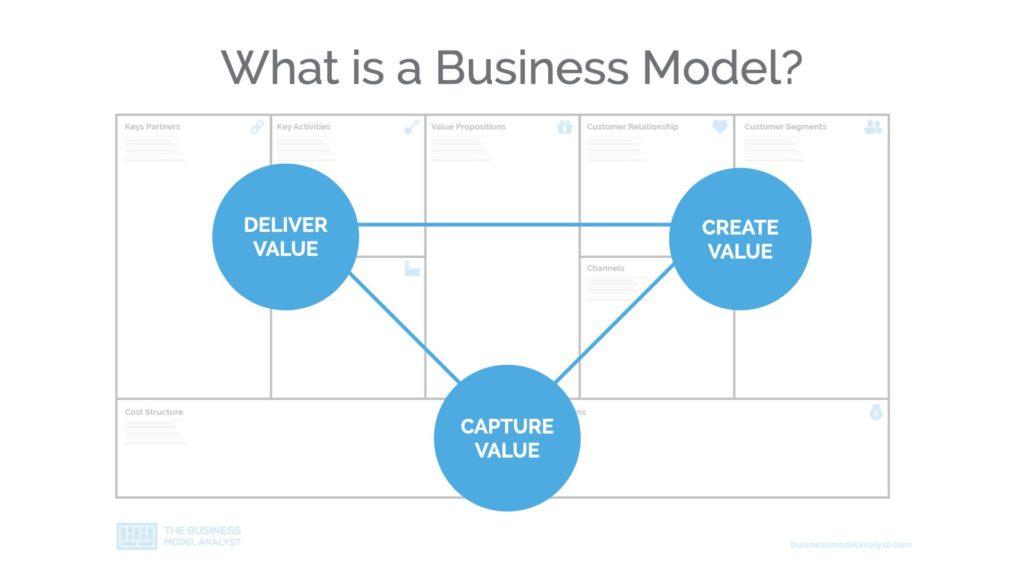
By definition, a business model describes the logic of how a company creates, delivers, and capture value.

There are three key components within a business model: creating value, delivering value, and capturing value. This shows that the business model doesn’t revolve around money. It revolves around value. This Business Model definition was created by the Swiss Consultant Alexander Osterwalder as a result of his PhD thesis, entitled The Business Model Ontology, in which he researched different business model definitions to create a single one. It was this document that later gave birth to the popular Business Model Canvas tool.

How a business model works
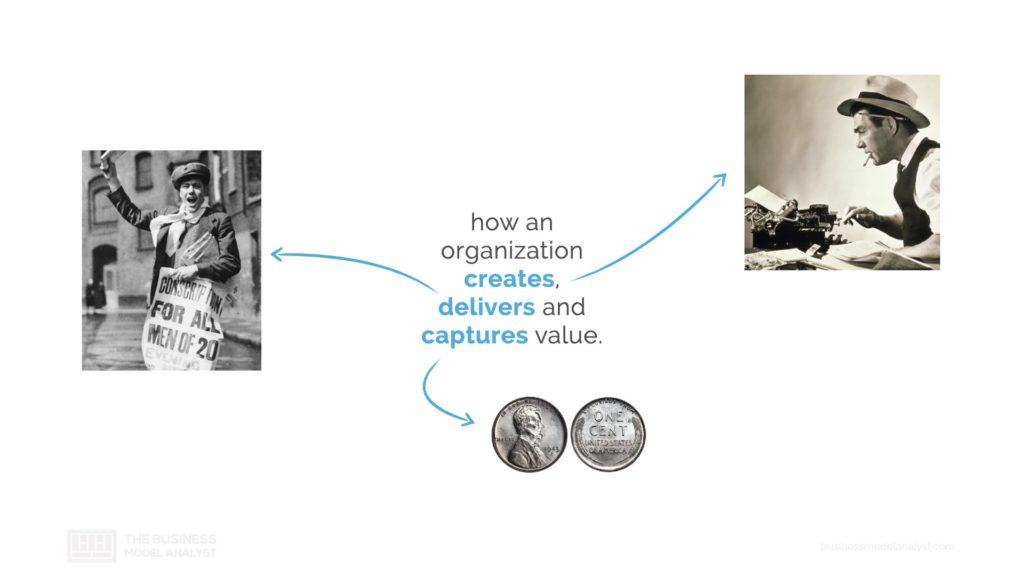
To better understand how a business model works let’s look at an example. If we look at the news industry in the 20th century, how the three main components of a business model worked? How would the news industry, or a news company, created value? They would have journalists write articles and produce newspapers. How would they deliver this value? They would have paperboys that would go around delivering newspapers around neighborhoods. And how would they capture value? They would have companies that would advertise, place ads in these newspapers
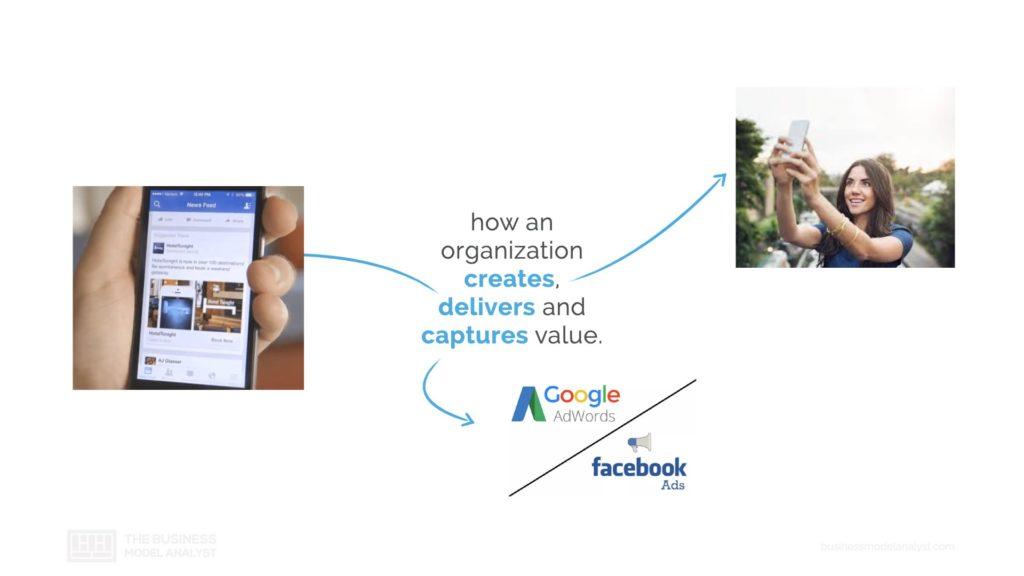
Now, what about in the 21st century? How does the industry news look like today? It’s the exact same three pillars, creating, delivering, and capturing value. But it’s done in a different way. so, rather than having journalists create value today, we create value, we the people who use platforms like Google and Facebook. We are the ones creating content. It’s being delivered on these social platforms, like Google, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, or Youtube. These are all platforms that are delivering the content that we create. And is the value of that delivered content being captured? It’s being captured through advertisements, Google Ads, Facebook Ads, Youtube Ads. So, the process still the same, but obviously has been updated and innovated in a different way to fit in with the technology of the 21st century.
Again, if we look at an example of a grocery store from the 20th century, they would create value by accumulating all the goods and products from farmers, from butchers into one location. They would deliver value by basically allowing people to come into that location and buy whatever they would want in the quantity they needed. And they would capture that value in the cash register.
Today, in the 21st century, again, still the same process, but done in a different way. So companies like HelloFresh and Deliveroo are pretty much revolutionizing the way we get groceries and the way we eat. So, for example, HelloFresh, the way they create value by creating recipes, and they deliver those recipes to you so you don’t have to actually go to a store or physical location. How do they capture that value? You subscribe online for a monthly fee on their website with your credit card.
So again, the process still the same, creating, delivering, and capturing value, but we can innovate the way it’s being done. That’s how business model innovation works. So again, to really emphasize, it’s all about value. It’s not about money, it’s about value.

Check out our super guide about business models in the 20th vs 21st centuries with 13 differents industries business models and how they have evolved through time:

Check it out by clicking here.
Business Model Objectives
A business model is a high-level plan of how your company sells and operates. In practice, it includes baseline aspects of each and every business, such as value proposition, processes, target audience, offers, strategies, organizational structure, operational and political processes. The objective is to identify the product and/or service to be sold, as well as the public to whom it will be offered, while anticipating the expenses involved in the entire production and sale process, in pursuit of the established goals. According to management guru Peter Drucker, “a business model is supposed to answer who your customer is, what value you can create/add for the customer and how you can do that at reasonable costs”. In general, in addition to offering a direction for the enterprise, the business model also serves to attract investors, recruit talent, and motivate the team. A business model is an important tool in today’s corporate world.
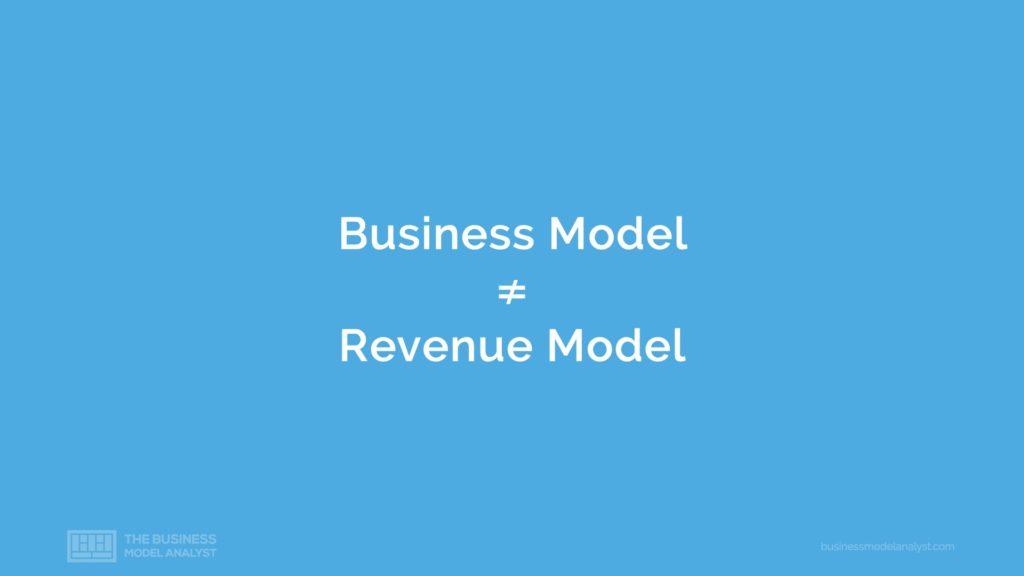
Is Business Model the same as Revenue Model?
The vast majority think that a business model is the same thing as a revenue model. A revenue model describes how a company makes money through its various revenue streams and that’s not the business model. A revenue model is part of the business model, but it’s not the entire thing. There’s much more to the business model and that’s what we are going to cover next.
Check out our super guide about revenue models with 21 models explained to help you choose the best revenue model for your company:

Check it out by clicking here
When is a business model sustainable?
When it comes to business modeling, the following equation is extremely important: Created Value > Captured Value > Cost of Delivery
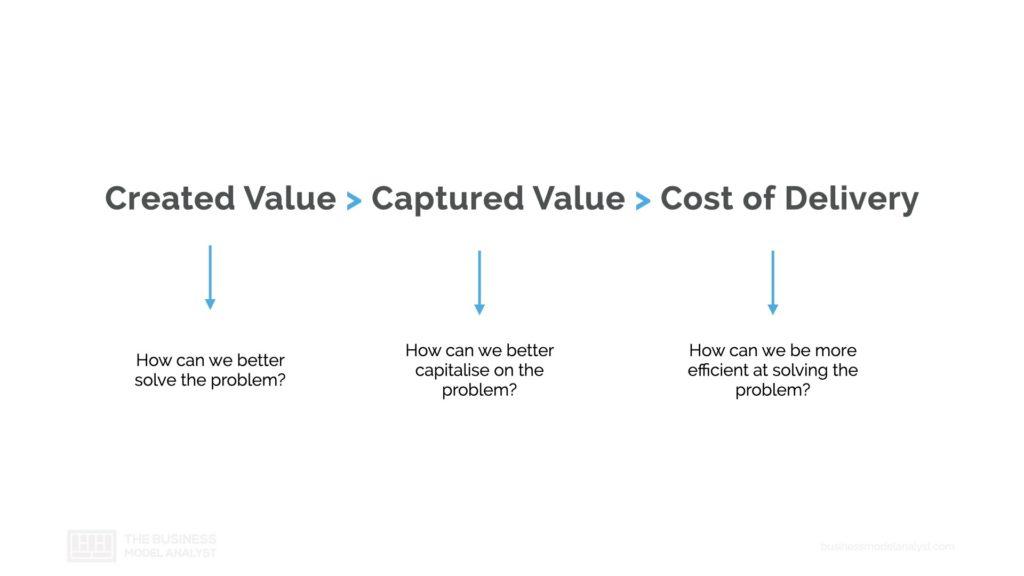
We have to create more value than we capture and we have to capture more value than it costs to deliver that value. A business model will only be sustainable if this equation holds true. In order to create a sustainable business model you need to ask yourself the following questions:
- How can we better solve the problem? (Created Value)
- How can we better capitalize on the problem? (Captured Value)
- How can we be more efficient at solving the problem? (Cost of Delivery)
What’s interesting is that when we look at business model innovation, we can innovate in each of these aspects.
What are business model components?
The business model has components related to marketing/sales (create value), operations (deliver value), and finance (capture value). Although the Business Model conceptually has three main components, the business model canvas, which is the most popular tool for business modeling, has a more detailed approach based on 9 construction blocks.

The 9 blocks of construction are:
- Customer Segments
- Value Proposition
- Distribution Channels
- Customer Relationship
- Revenue Streams
- Key-Resources
- Key-Activities
- Key-Partners
- Cost Structure
To better understand each of these blocks you can click on the links above to read more in-depth.
What is the business model process?
The process is known as business modeling or business model design has essentially two parts:
- business model development
- business model validation
The business model development can be better achieved by using the business model canvas. There’s a specific order to develop a business model using the canvas.
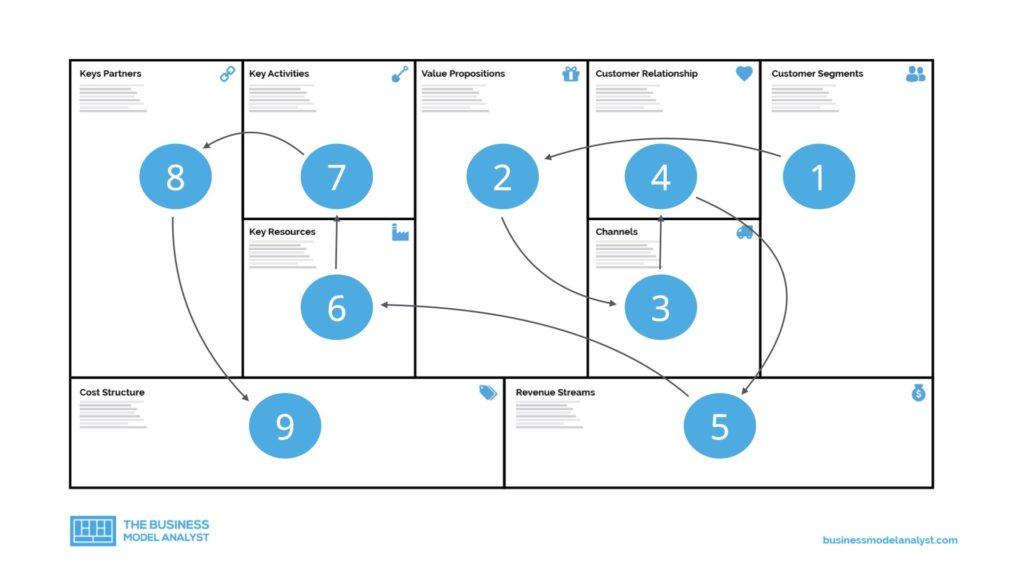
The order considers that a business model must approach first the desirability of the business. Does the customer want it? Can we create this? Second, you must approach the feasibility of the business. Can we operationalize this? Can we deliver this? And last, you need to prove the economic viability of the business. Can we capture profits?
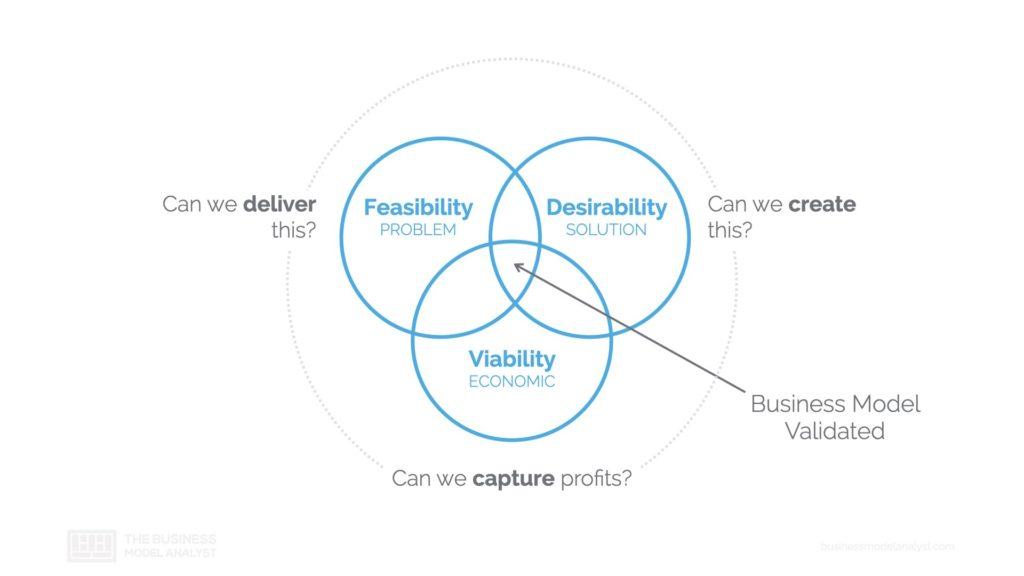
This is already part of the validation process, which is the second part of the business model development process. You need to assume that every part of your business model is a hypothesis that needs to be validated. The only way to validate your business model is by testing your assumptions. A more detailed approach to the business model testing cycle can be seen below.
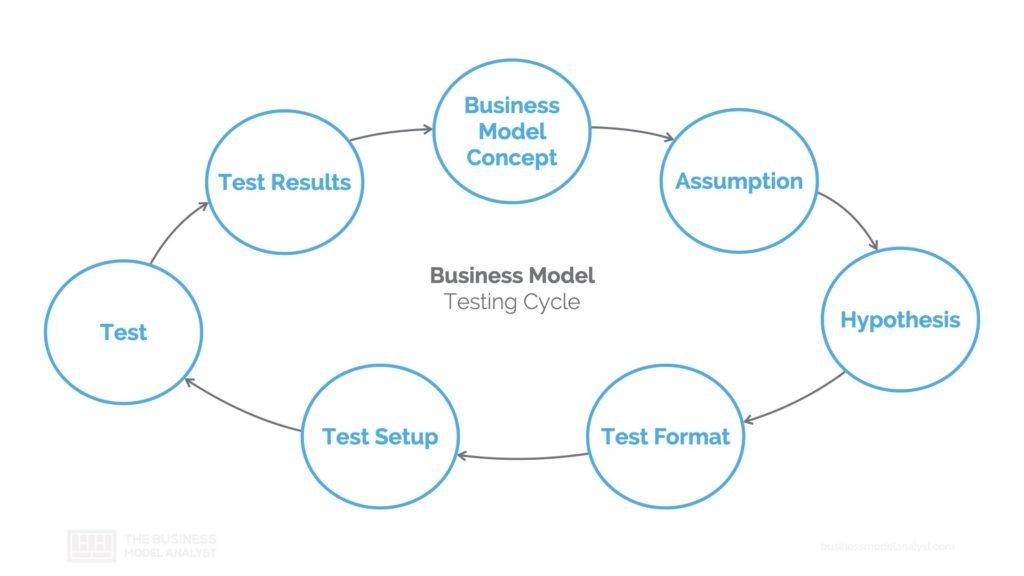
Only after you have tested every single strategy for every single construction block you can have a better chance of a successful business model. Check out our super guide about business testing with different tools and approaches to test your business model hypothesis and help its development.

Check it out by clicking here
How to develop a business model
The best way to put in practice the business model development process is by gathering people of different expertise into a visual workshop. The development of a business model involves the use of visual tools, such as the business model canvas, which works as a common language between participants.
What is business model transformation?
New business models emerge or transform base on shifts in technology and consequently in customer behavior. New technologies force us to experience things in a completely new way. From car ownership to mobility apps, from in-class education to online education, from commercial hours malls to 24/7 online shopping.
Customers’ needs are still the same, but their behavior has changed. So the question you need to make is How does my business adds value in the new consumption era? You can read more about Transitional Business Models in our Super Guide below:

Check it out by clicking here.
What is a business model example?
A good example of a business model can be seen in the business model canvas of the Netflix
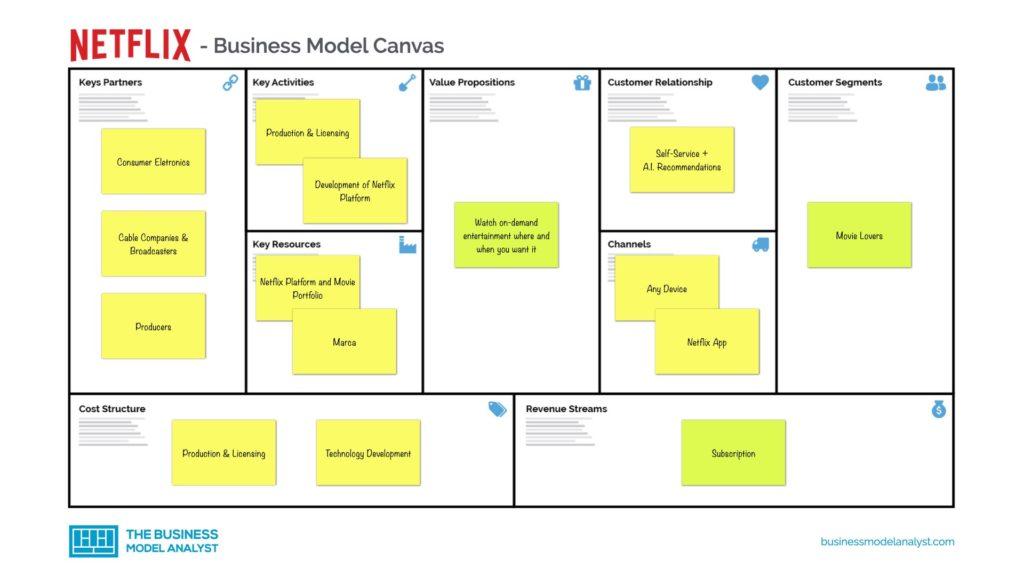
What is business model analysis?
There are different ways of analyzing and assessing a business model. A very common approach is using the SWOT Analysis to understand the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
You Can do the SWOT Analysis of your Business Model using our Business Model Assessment Spreadsheet
Check it out by clicking here
Types of business models
In fact, there are as many business models as there are types of business developed. Some of the most common are:
- Advertisement: offers free information or service to the final customer and its source of revenue are the ads published on its platform.
- Affiliate Marketing: promotes a partner’s product and receives commissions on sales made through its publicity.
- Agency-Based: a company specialized in providing non-essential services to other companies, such as marketing and advertising.
- Aggregator: when the company sells several services aimed at the same niche, under the same brand and the revenue comes from commissions, such as Uber and Airbnb, for example.
- Blockchain: it is a digital and decentralized database, that is nobody’s property, but that anyone can be part of and contribute to, in P2P interactions.
- Brick-and-mortar: a company with a physical space where the consumer goes to make his purchase.
- Bricks-and-clicks: an operation with an online and physical presence. The consumer can buy via the internet and collect it in the store.
- Crowdsourcing: here, users contribute with the content and service provided through the platform, in collective creation, such as Wikipedia.
- Data Licencing/Data Selling: sell its users’ data for analysis and/or advertising.
- Distributor: buys from the manufacturer and resells to the retailers or to the final customer.
- Dropshipping: it is a kind of e-commerce without stock, something like a virtual showcase. The products are displayed in its online store but are delivered and invoiced to the customer by the suppliers. The source of revenue commissions.
- eCommerce: sells products in an online store.
- Franchise: uses a business model and a brand already established in the market, paying royalties to the franchisor.
- Freemium: typical of Internet products, it is the business model in which the company offers something for free and charges for any extra product/service. In general, there are different plans for different benefits.
- High Touch: based on human interaction, with the perceived value in the quality of the service provided and in the trust between the parties, as a consultancy service, for example.
- Low Touch: with minimal human interaction, it lowers costs by reducing investment in human resources, like Ikea, for example.
- Manufacturer: manufactures a product from raw material. In general, it sells to a client who will resell to the final customer, but it can also sell directly to them.
- Network Marketing: multi-level marketing that involves a pyramidal structure, in which salespeople are commissioned for what they sell directly as well as for what the salespeople recruited by them do. There is no store. The audience is reached directly by the sales team.
- Nickel-and-dime: the price of its basic product is as low as possible. All other associated services are charged.
- Online Marketplace: an internet-based company that aggregates different suppliers who compete with each other, usually by price. The source of revenue is the commissions on each product sold on its platform.
- Peer 2 Peer Catalyst/Platform: it is a platform in which the two parts of a business interact directly with each other, without mediation, such as OLX.
- Retailer: buys from a distributor or wholesaler and sells to the final customer.
- SAAS, IAAS, PAAS: software or platforms offered as a service, that is, the customer pays according to the number of resources they use.
- Subscription: the objective is a long-term contract in which the customer regularly pays for services, usually a monthly fee.
Which business model is best?
There’s no such thing as the best business model. There are plenty of successful company cases in many different business model types. But business models that use recurring revenue models such as subscription or SaaS or that uses network effects such as marketplaces and platforms are powering the most successful businesses.
Can you copy a business model?
Yes, you can. The essence of creating, delivering, and captures can be

Can you protect a business model?
Business models can’t be patented but the technology that supports them can. This has been increasingly more difficult as technology becomes more and more accessible and diversified. Just ask yourself: Can Google’s business model be patented? Can Netflix’s business model be patented? Can Facebook’s business model be patented? Can Amazon’s business model be patented? No, it can’t. But the reason you just don’t create another Facebook by creating another company with the same business model is because of how hard it is to create similar technologies or execute similar strategies.
Can you license a business model?
You can’t license business models, but you can license brands, processes, and other business model parts. This is usually done in the form of franchises. Companies like McDonald’s, Subway, and Pizza Hut all use the franchise business model.
Business model advantages
As a general rule, business models often include everything related to the creation, production, and sale of the product or service, information about the target audience and distribution of the product, as well as what the company’s revenue source will be, that is, how the consumer will pay for that good. It is, after all, a “recipe” to be followed by the project team. This recipe usually starts with the value proposition – a description of the products and/or services that will be offered, by demonstrating what differentiates them from other competitors in the market. Besides, it contains the costs involved, sources of financing, a definition of the target audience and the marketing strategy to reach it, projections of revenues and expenses, an analysis, even if brief, of the competitors, and a description of possible partnership opportunities. The main purpose of a business model, therefore, is to allow the company to deliver value to the customer at a sustainable cost. As the business model is able to analyze all the details of the enterprise even before it is put into practice, the chance that this objective doesn’t get reached is very remote.
business model canvas template
You can download a business model template in PDF hereYou can download a business model template in Powerpoint (PPT) here
Why Business Model Maters
Business model matters because they allow you to create business strategy and innovations in a more holistic way, going beyond revenue models or technology innovation.
Bottom line
Surely, there are many more business models other than those above. And, as market demands change, new models are created. Besides, it is worth remembering that most companies today don’t operate under a single business model. It is quite common to see a combination of several. The business model you choose depends on your company’s needs and the value you want to create for the stakeholders involved, especially for your target customer. Finally, don’t forget that any business, no matter how successful and established it may be on the market, need to revisit and update its business model and strategies in order to understand and get prepared for changes and trends. Any failure in this assessment can threaten the future of the company and its investors.
Check out our Super Guides Combo and Save Big Time!

More details by clicking here.