In the relatively short time since the concept has been around, Point-of-Sale (POS) loans have been instrumental in reshaping the consumer world as we know it. Thanks to the fact that they offer Buy Now Pay Later services on consumer purchases, it effectively gives people more purchasing power. One of the foremost purveyors of this service is Afterpay. So here, we’ll be taking an in-depth look at the Afterpay business model to learn more about how the company operates.
Exploring the simple yet unique operating system that this brand uses is vital because it can provide much-needed insight into how Afterpay has managed to distinguish itself from the rest of the pack and become a world-leading provider in only a few short years.
With that said, here’s everything you need to know about the business model of one of the most popular Buy Now Pay Later platforms on the globe currently!
Contents
A brief history of Afterpay
More formally known as Afterpay Limited, Afterpay was founded by Nick Molnar and Anthony Eisen, two individuals who initially met as neighbors. Molnar always had the makings of an entrepreneur, as he had been importing and selling items from the tender age of 14.
They formed a powerful partnership and launched an initiative called Innovative Payments in 2014. Innovative Payments was what would lay the foundation for the Afterpay brand that the world has come to know today.
The Australian financial technology company acquired its first retail customer in 2015. This was the fashion group, Princess Molly. This move would turn out to be a stroke of genius, as it made Afterpay an instant hit. The company was especially attractive to retailer customers who didn’t have credit cards and offered a breath of fresh air due to its unique deviation from the norm.
This move was so successful that it not only increased the basket size of the brand significantly, compared to its competitors, but it also lifted their revenue by as high as 15%.
What’s more, adopting this method of approach proved so productive that, in less than four months after bringing on their first retail customer, Afterpay was able to easily raise its first $8 million.
Its impressive Buy Now Pay Later services continued to expand as it spread from Australia to Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, and, eventually, New Zealand.
Afterpay would go on to merge with one of its technology suppliers, Touchcorp, in June 2017. The union of these two companies became known as the Afterpay Touch Group. However, just a little over two years later, in November 2019, the company’s name was again changed to Afterpay Limited.
To further enhance the smooth operations of the Buy Now Pay Later company, Afterpay and Square, Inc., the American payments company announced that the former would be purchased by the latter. Afterpay Limited was to be sold for US$29 billion. This transaction was finally completed on January 31, 2022.
Who Owns Afterpay
Following the acquisition of Afterpay Limited by Square for US$29 billion in 2022, the Buy Now Pay Later platform is now officially owned by the United States-based mobile payments titan.
The price that the merger went for was 42 times the revenue of Afterpay, and has officially become the most significant merger ever announced in Australia. The two co-founders, Anthony Eisen and Nick Molnar, had a stake of 6.87% and 6.72 in stocks in the company sold respectively. As such, they’re expected to be paid out in stocks. The founders have also joined Square since the completion of the transaction.
Square operates a similar paradigm to Afterpay, as it leverages a single, easy-to-use system to facilitate smooth aggregation and payment for merchant services and mobile payments. Square is owned by Jack Dorsey, the creator and former owner of Twitter, the social media platform.
Afterpay Mission Statement
The mission statement of Afterpay is, “To power an economy in which everyone wins.” This is in keeping with the brand’s founding principle of empowering consumers to do more and readily access the things they want and need to live their best lives. Afterpay prides itself on offering consumers the ability to maintain financial wellness and complete control through the proper portioning of payments, whether during in-store or online purchases.
How Afterpay makes money
Like the vast majority of other Buy Now Pay Later platforms, Afterpay Limited predominantly makes money through merchant fees made on each purchase and through the levies imposed on customers for late payments. Here’s more on these two parameters.
Merchant Fees
Again, as is the convention with most Buy Now Pay Later service providers, a merchant has to pay a certain sum for every transaction successfully facilitated by Afterpay.
The standard charge here is 30 cents plus a variable fee. Depending on numerous unique elements, the variable fee can fall between 4-6%. However, the exact fee that a merchant has to pay will be determined by the value and volume of all the transactions carried out. But typically, merchants that see higher traffic and sales or who sell more expensive goods and products tend to pay lower fees.
It bears mentioning that the variable fee charged on merchant purchases is what generates the highest revenue for Afterpay.
Another point worthy of note is that a merchant can opt to sell all their items without leveraging Afterpay. However, according to Afterpay, offering the installment payment option can increase the buyer conversion rate significantly. Also, it can boost order value by as much as 20%.
But, beyond helping merchants make more sales, Afterpay imposes a merchant levy to mitigate the risks of a consumer defaulting on their payments.
Late Payment Fees
Afterpay also has a late payment policy that it implements if and when consumers do not fulfill their obligations when due. As such, any individual who doesn’t make the stipulated payment according to schedule has to cough up this sum. How much a consumer is expected to pay for late payments varies, depending on some factors.
As an example, the initial late payment fee is $10. However, an additional $7 may also be charged if the consumer still hasn’t lived up to their responsibility seven days past the initial due date.
Also, worth noting is that orders that fall below $40 don’t come with more than the $10 late payment fee, no matter what. But, for orders in the range above that price tag, the late payment fee gets capped when it reaches 25% of the original order value. The late payment fee can also be capped when it stands at $68.
Afterpay’s Business Model Canvas

Now, we’ll be taking a look at the Afterpay business model canvas through various crucial parameters.
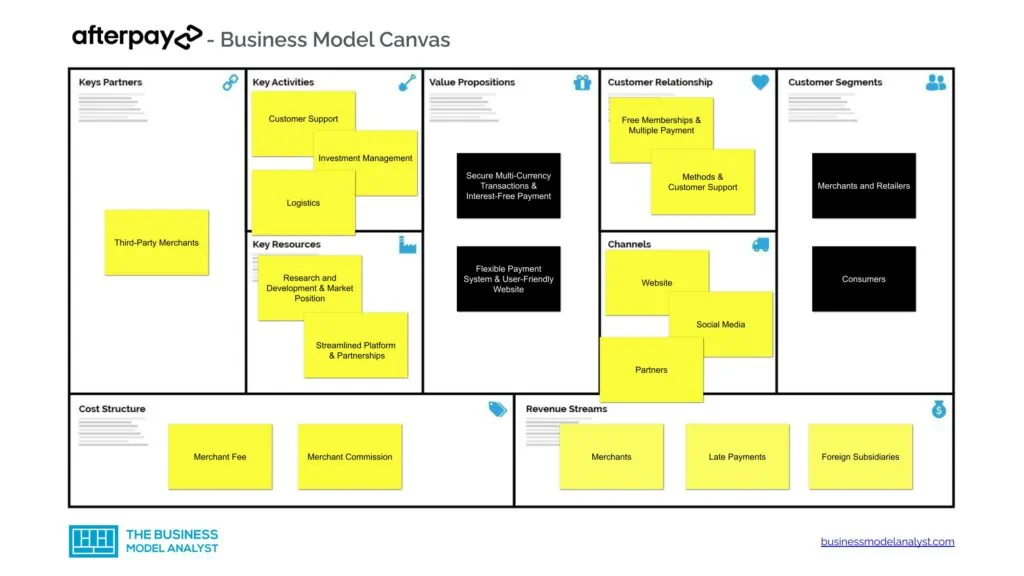
Afterpay’s Customer Segments
As a company committed to creating value in the Buy Now Pay Later service industry, Afterpay has a wealth of clients. Some of the most important customer segments are:
- Merchants and Retailers: Retailers and Merchants represent one-half of the important coin that makes the Afterpay system viable. This is because the goods and products they make available are key things that attract consumers to the platform. As such, Afterpay has a long list of businesses that it affiliates with and encourages bringing items to its “pay later” system;
- Consumers: The other half of the all-important coin, these are the people who leverage the flexible payment system that Afterpay offers. The company supports this class of individuals by making attractive packages and an optimally streamlined operation available.
Afterpay’s Value Propositions
Afterpay remains a dominant presence in its niche thanks to the vast array of value propositions that it makes available to consumers. Afterpay value propositions consist of:
- Secure Multi-Currency Transactions: Unlike many of its counterparts, Afterpay doesn’t employ a fixed fiat through which all platform transactions must occur. Rather, it openly accommodates a myriad of currencies. This actively encourages the use of the platform with minimal planning;
- Interest-Free Payment: Also unlike most of its competitors, Afterpay refrains from charging its users for its services. As this helps more people get increased value for their money with the platform, the interest-free payment system has gone a long way in making the platform popular;
- Flexible Payment System: Afterpay allows consumers to make payments for the items they purchase in four different installments. This relieves pressure without limiting purchasing power and thus makes the platform very attractive;
- User-Friendly Website: The highly engaging and interactive UI of the brand’s platform has also gone a long way in increasing the recognition and acceptance of the brand. This is because it makes their services that much easier to utilize.
Afterpay’s Channels
Afterpay utilizes three channels to engage its target audience. These are:
- Website: The most readily available channel through which consumers can freely interact with Afterpay is its website. As was mentioned earlier, this interface is highly engaging and as such greatly minimizes the need for contact with a physical individual;
- Social Media: This company can also be reached through any number of social media platforms, most notably Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. In most cases, these outlets are leveraged to make minor complaints or get updates on the latest offerings from the brand;
- Partners: Afterpay can also be reached, albeit in a rather limited capacity, through its partners. These entities run advertisements for the brand and can offer a viable point of contact, should consumers request one.
Afterpay’s Customer Relationships
As a brand that shows that it deeply values its consumers, Afterpay Limited provides three points through which individuals can build a long-lasting relationship with the brand. These are:
- Free Memberships: Afterpay doesn’t place a levy on the admittance of individuals into its flexible payment system. And, as its registration process is fast, simple, and hassle-free, the brand presents itself as a platform that anyone can utilize on a dime;
- Multiple Payment Methods: This company also ranks as one of the Buy Now Pay Later platforms with the most extensive array of payment methods. As most consumers don’t have to inconvenience themselves when making payments, the brand positions itself as a more convenient solution on this front;
- Customer Support: The organization also backs its services up with a meticulous and efficient customer support system, so consumers can always rest assured they are in good hands.
Afterpay’s Revenue Streams
This Buy Now Pay Later company generates income through three main avenues. Afterpay revenue streams consist of:
- Merchants: Afterpay charges merchants and businesses for making use of its services. The more high-end the Afterpay service the merchant relies on, the more the brand charges. Additionally, Afterpay also charges these entities for every transaction performed through them. This is where the larger percentage of the company’s revenue stems from;
- Late Payments: While Afterpay doesn’t charge consumers for leveraging its services, it does impose a penalty on those who default on their payment schedule. The sum generated from this source is also quite considerable as well;
- Foreign Subsidiaries: The company also generates a modest income from the operations of its subsidiaries. One such subsidiary is Clearpay. This establishment operates out of the United Kingdom
Afterpay’s Key Resources
The key resources that this brand relies on to thrive are:
- Partnerships: Afterpay makes strategic partnerships and uses these to the best effect to provide consumers with high-demand items with a flexible payment structure;
- Research and Development: The company also invests heavily in its research and development team. The ultimate aim of this is to find even more efficient ways of catering to the ever-changing needs of consumers;
- Market Position: In the few years that Afterpay has been around, the company has gained tremendous brand recognition. This it uses to its advantage to push its services into new areas;
- Streamlined Platform: The well-laid-out arrangement of the Afterpay platform also works greatly in its favor to drive traffic and conversion upwards.
Afterpay’s Key Activities
The key activities of Afterpay range from:
- Customer Support: As one of the most important facets of the company, Afterpay extensively provides customer support by ensuring the security of their consumers during and after transactions;
- Investment Management: Because Afterpay is heavily reliant on its investors, the company also takes steps to manage and protect the interests of its sponsors;
- Logistics: Afterpay is also tasked with attending to the finer aspects of various logistical elements. These include but aren’t limited to the distribution of finance, implementation of sponsors, and production.
Afterpay’s Key Partners
Afterpay key partners consist of:
- Third-Party Merchants: Third-party merchants account for the most significant portion of Afterpay’s partners. These merchants function in various capacities and are either responsible for providing funding for the company or creating an advertisement platform for the brand; ● Investors: Investors are another critical group of partners for this brand. Some major names that have invested in Afterpay over the years include Tencent, Coatue, and Mitsubishi, to mention a few.
Afterpay’s Cost Structure
Afterpay’s current operating system offers two noteworthy elements in the cost structure department. These are:
- Merchant Fee: The merchant fee is the first mark-down this road. Fixed at a flat fee of 30 cents, every business, and retailer active on Afterpay is expected to pay this sum;
- Merchant Commission: To further complement the merchant fee, a commission is also charged on every transaction that a retailer successfully carries out. Depending on the specifics of the transaction, what a merchant pays as a commission can be as high as 4 to 6% of the item(s) value.
Afterpay’s Competitors
The Buy Now Pay Later industry is highly saturated at the moment. This leaves Afterpay with a lot of competition. Some of the most notable ones are:
- Sezzle: Sezzle was founded by Charlie Yuakim who also serves as the current CEO of the establishment. Sezzle offers serious competition to Afterpay because it doesn’t run hard credit checks and allows consumers to reschedule their late payment once, free of charge;
- Klarna: Founded in 2005, not only does Klarna operate in the same space as Afterpay, but how they offer their services is also remarkably similar as well. Klarna requires that consumers make their first payment at the POS and the remaining payments at two-week intervals;
- Affirm: The brainchild of Max Levchin, Nathan Gettings, Jeffery Kaditz, and Alex Rampell, Affirm was founded in 2012. This Buy Now Pay Later platform extends a considerable amount of credit and is remarkably flexible with its repayment schedule.
Afterpay’s SWOT analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Afterpay:
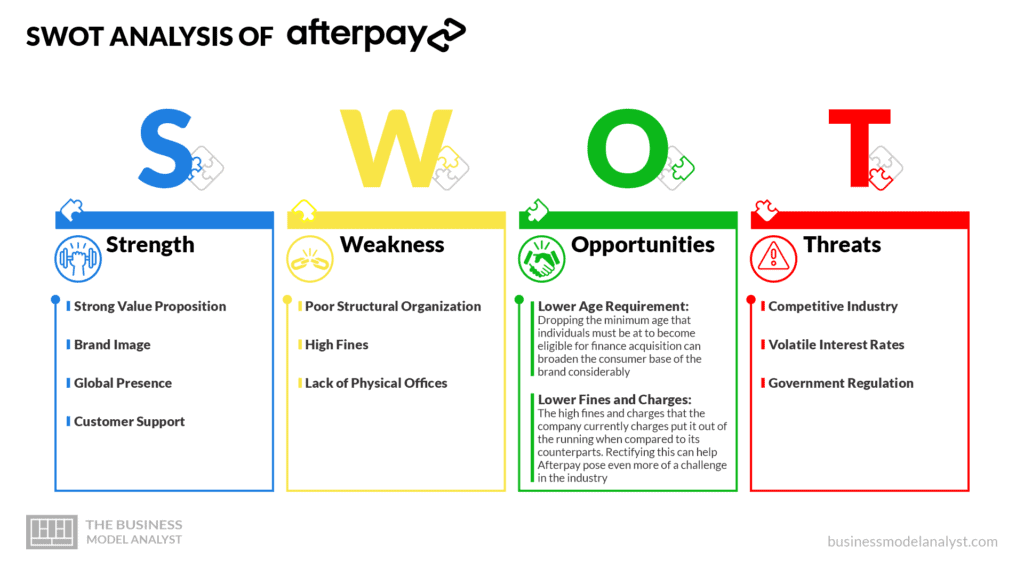
Afterpay’s Strengths
- Strong Value Proposition: Thanks to the strong and unique value proposition that Afterpay adopts, they can more consistently maintain their ground in the Buy Now Pay Later industry;
- Brand Image: While not yet a decade old, the company has worked to build a strong image that’s synonymous with reliability, trust, and integrity. This continues to work in their favor to attract new consumers;
- Global Presence: Afterpay has managed to establish a strong multinational presence. This they use to their advantage to easily penetrate the market of the competition;
- Customer Support; The fact that the brand is quick to address consumer complaints has earned them endorsements from numerous high-profile figures.
Afterpay’s Weaknesses
- Poor Structural Organization: The organization paradigm that this company employs appears unfit to properly execute the services that it proffers;
- High Fines: The fines that Afterpay charges for late payments happen to be on the high side, compared to its competitors;
- Lack of Physical Offices: As the company doesn’t have a brick-and-mortar location ascribed to them, some potential users are discouraged.
Afterpay’s Opportunities
- Lower Age Requirement: Dropping the minimum age that individuals must be at to become eligible for finance acquisition can broaden the consumer base of the brand considerably;
- Lower Fines and Charges: The high fines and charges that the company currently charges put it out of the running when compared to its counterparts. Rectifying this can help Afterpay pose even more of a challenge in the industry.
Afterpay’s Threats
- Competitive Industry: Afterpay operates in a highly condensed space. What’s more, many of the competitors operate business models that are an improvement on those of Afterpay;
- Volatile Interest Rates: The constant fluctuation of interest rates makes it challenging for the brand to take a consistent position that its consumer base can readily identify it with;
- Government Regulation: With many global and national government agencies implementing restrictive policies for private financers, there’s always the possibility that the brand will get choked out by these regulations.
Conclusion
The Afterpay business model is an ingenious method of operation that deserves a lot of applause for its inspired approach to the Buy Now Pay Later industry. While the brand has suffered more than its fair share of hiccups in the past, the future remains largely positive for it. We look forward to seeing how Afterpay will evolve under its new ownership.

