The Accenture business model focuses on an “as-a-service service” mode of service delivery based on operations, technology, interaction, strategy, and consulting. If you’re hearing about Accenture for the first time, this article will provide comprehensive details to help you understand what the firm does.
Contents
A brief history of Accenture
Accenture is a leading international professional services firm, also defined as Accenture PLC (NYSE: ACN). It helps governments and some of the leading businesses in the world develop their digital core, improve their operations, speed up growth, and boost citizen services. With its headquarters in Dublin, Ireland, Accenture operates in over 200 cities in 120 countries. Accenture started as a technology and business consulting company of Arthur Andersen, an accounting firm, in the early 1950s.
The firm had conducted a feasibility analysis for General Electric to facilitate the installation of a computer at Appliance Park in Louisville, Kentucky. The result was G.E.’s UNIVAC I printer and computer installation, which many people believed was the inaugural commercial computer use in the U.S. Then, the firm was known as Andersen Consulting. Arthur Andersen and Andersen Consulting split in 1989 to operate separately under Andersen Worldwide Société Coopérative (AWSC).
Across the 1990s, tension was rising between the two entities. Arthur Andersen earned up to 15% of Andersen Consulting’s profits annually. Arthur Andersen launched a new business consulting firm, Arthur Andersen Business Consulting, to compete with Andersen Consulting. The dispute between Arthur Andersen and Andersen Consulting escalated in 1998 when the latter placed the 15% transfer payment for that and future years in escrow. The firm issued a breach of contract claim against Arthur Andersen and AWSC.
The dispute was concluded in 2000 following mediation with the International Chamber of Commerce. Andersen Consulting discontinued all contractual links with Arthur Andersen and AWSC and paid the escrow-held sum of $1.2 billion to Arthur Andersen. Andersen Consulting then changed its name to Accenture. Accenture’s IPO in 2001 was $14.5 per share.
The shares started trading on the NYSE, with Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs serving as their lead underwriters. The company evolved over the years, and in 2020, reports indicated Accenture’s intention to acquire Broadcom’s 300-person Symantec cybersecurity services. Accenture would later acquire Callisto Integration, a technology and consulting firm based in Canada, and Byte Prophecy, a data analytics firm based in Ahmedabad.
In 2021, Accenture acquired Imaginea Technologies, an agile development and cloud-native company, and Infinity Works to improve the firm’s Cloud First division. Accenture would later acquire Trivadis AG, an I.T. services provider, and Cygni, a full-stack development and cloud-native company.
Who Owns Accenture
As seen below, various shareholders own a certain percentage of shares in Accenture, with Vanguard Group Inc being the biggest individual shareholder. Vanguard Group owns 58.47M shares, with a current value of $16.60B.
- Institutional shareholders 78.86%
- Retail investors 28.22%
- Accenture’s insiders 0.92%
Accenture Mission Statement
The Accenture mission statement is “To help our clients create their future.”
How Accenture works
Accenture operates under the following reportable business divisions.
Technology, media, and communications
Accenture provides industry-specific solutions to help clients speed up and deliver digital transformation while enhancing business results. Clients can seize opportunities facilitated by merging computing, content, and communications through the firm.
Financial services
Accenture collaborates with clients to address growth, cost, and profitability pressures, industry consolidation, regulatory changes, and the impact of adopting new digital technologies. The firm focuses on capital markets, insurance, and banking industries.
Health and public service
Accenture helps clients deliver enhanced health, economic, and social outcomes to their customers. The company focuses on the public and health service industries for nonprofit organizations and governments.
Products
Accenture allows clients to revolutionize their firms and boost their reverence in the digital industry. It focuses on the life sciences, industrial, travel, retail, and consumer goods industries.
Resources
Accenture works with clients to build and enforce innovative strategies, integrate digital technologies that help them gain a competitive edge, boost operations, and manage intricate change initiatives. The firm focuses on mining, metals, utilities, forest products, chemicals, and energy industries.
How Accenture makes money
Accenture makes money by providing professional services, which are:
Consulting revenues
Digital evolution projects meant to help clients boost business agility has triggered revenue increase in this segment.
Outsourcing revenues
Accenture generates revenue through support and maintenance. Consulting projects are critical for creating a robust channel of outsourcing projects.
Accenture Business Model Canvas
The Accenture Business Model can be seen in the business model canvas below:
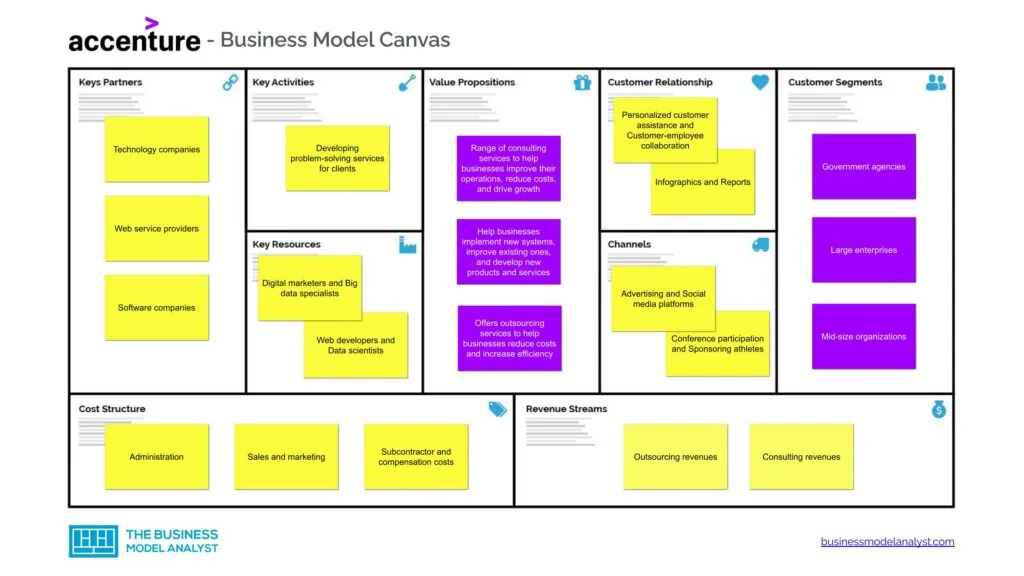
Accenture Customer Segments
Accenture customer segments are all organizations that require management consulting services. These include:
- Government agencies
- Large enterprises
- Mid-size organizations
Accenture Value Propositions
Accenture’s primary value propositions are:
- Accessibility: Accenture has invested up to $2.5 billion in acquisitions and emerging technologies, allowing it to incorporate diverse capabilities into its service menu. For instance, the firm acquired Javelin Group in 2015 to boost its retail expertise;
- Customization: Accenture provides customization through its service and knowledge specificity. It guarantees market relevance and local execution in its offices in more than 120 countries. Accenture also operates in over 40 sectors; nearly half of its staff have certified industry skills or are aligned with a particular market. This enables the company to offer highly customized guidance;
- Innovation: Accenture maintains a development and research organization, Accenture Technology Labs, that specializes in identifying and developing new technologies. The firm also runs the Accenture Institute for High performance. The program helps create modern market-ready solutions and insights for customers;
- Brand: Accenture is one of the largest consulting firms in the world. It’s also among the leading and biggest independent technology firms.
Accenture Channels
Accenture’s core channel for client acquisition is through its personal relationships with its partners. The firm promotes its services through:
- Advertising
- Social media platforms
- Conference participation
- Sponsoring athletes
Accenture Customer Relationships
Accenture customer relationships consist of:
- Personalized customer assistance
- Customer-employee collaboration
- Infographics
- Reports
Accenture Revenue Streams
Accenture’s revenue streams consist of:
- Outsourcing revenues: Income generated from services and capabilities offered to manage and transform clients’ systems and the running of business functions;
- Consulting revenues: Income from technology, management consulting, and systems integration services.
Accenture Key Resources
Accenture’s key resources consist of:
- Digital marketers
- Big data specialists
- Web developers
- Data scientists
Accenture Key Activities
Accenture’s key activities consist of:
- Developing problem-solving services for clients
Accenture Key Partners
Accenture’s key partners consist of:
- Technology companies
- Web service providers
- Software companies
Accenture Cost Structure
Accenture’s cost structure consists of:
- Administration
- Sales and marketing
- Subcontractor and compensation costs
Accenture Competitors
- McKinsey & Company: McKinsey & Company is a management consulting organization that addresses technological, operational, organizational, and strategic issues. The privately-owned company works with firms focusing on natural resources, commodities, technology, and media;
- Boston Consulting Group, Inc: With over 14,000 employees working in 85 offices across the globe, Boston Consulting Group, Inc is among the largest private companies in America. The company serves some of the biggest companies, government agencies, mid-sized businesses, and nonprofit organizations. The company collaborates with experts in industries like industrial goods and financial services;
- Bain & Company: Established in 1973, Bain collaborates with clients in industries representing 90% of the international economy. Besides employing over 6,000 employees, the firm has collaborated with numerous local and regional organizations, governmental firms, private equity funds, and nonprofit groups. Bain & Company’s clients represent up to 75% of overall global equity capital;
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS): This multinational Indian company provides consultation and I.T. services. The company operates in 149 regions in 46 countries and has 50 subsidiaries. TCS had approximately 592,000 employees in 2021. The company collaborates with some of the largest firms in the world in its revolutionary journeys. It has been managing large data volumes in various silos;
- Recently, TCS collaborated with Qlik to develop a self-service insights and knowledge discovery platform. The platform coordinates data, allowing decision-makers in different departments worldwide to self-serve intuitive visual analytics and business intelligence through the cloud;
- Price Waterhouse Coopers (PwC): PwC is one of the world’s largest audit and accounting firms. It offers financial and risk advisory, tax analysis, and assurance services. Since it was established, the company has evolved to become one of the most trusted in the financial sector. PwC leverages its central service lines and knowledgeable resources to offer solutions to critical problems;
- IBM: This leading technology and computer company boasts a global presence. IBM offers consulting services and I.T. solutions like nanotechnology and mainframe computers. The company earned $57.35 in income in 2021, 70% from consulting and software segments. IBM has a vast product portfolio that other organizations depend on to streamline API management and cloud integration, support mobile development operations, and optimize applications;
- Deloitte: Deloitte is one of the leading consulting firms. It offers legal, tax, audit, consulting, and risk advisory services. The company had approximately 334,800 employees in 2021 and generated $50.2 billion in earnings. Deloitte depends on the North American market, even though it operates in more than 150 countries globally. The company’s client list features around 250 innovative firms;
- Genpact: Pramod Bhasin is the founder of this professional services company that helps organizations in over 30 countries reinvent operations, imagine processes, and enhance business results. Genpact’s services drive transformation and digital-based innovation. It has revolutionized numerous processes for many organizations globally;
The company is committed to speeding up the digital revolution to develop long-lasting solutions. Genpact’s artificial intelligence platform, Genpact Cora, combines analytics, data, and operational best practices to transform processes.
Accenture SWOT Analysis
Here is a detailed swot analysis of Accenture:
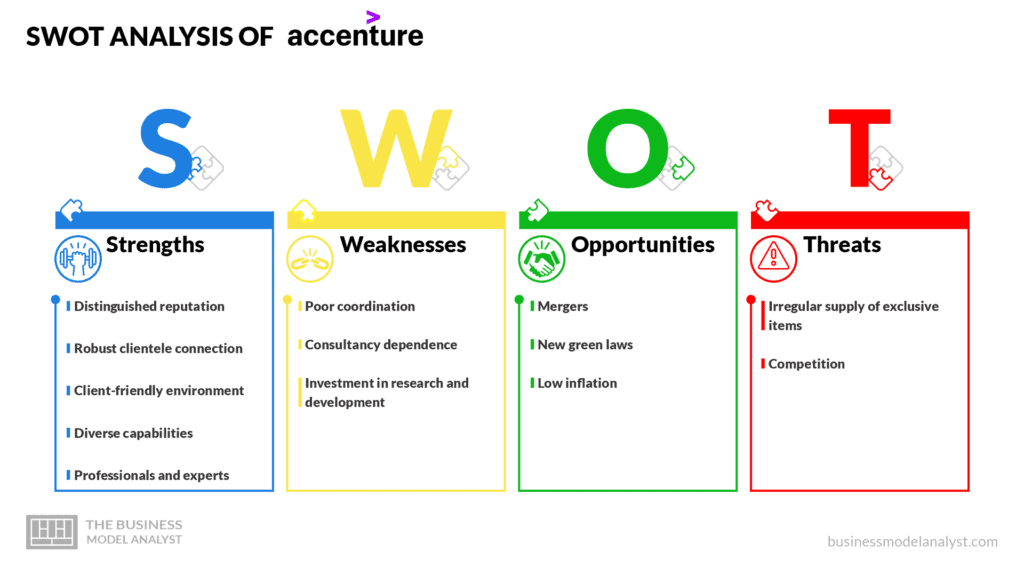
Accenture Strengths
- Distinguished reputation: Accenture is one of the largest companies in the world. Its focus on operational services, consultancy, technology, management, digital services, and high moral standards have resulted in high performance and revenues;
- Robust clientele connection: The firm collaborates with more than 500 multinational companies and has a vast global client base in different sectors;
- Client-friendly environment: Accenture’s user-friendly environment prioritizes clients’ needs, resulting in trusted and robust relationships;
- Diverse capabilities: following its operations in various sectors like public and financial services, technology, and communications, Accenture has diversified capabilities in its team. A trained and dedicated workforce in every industry differentiates Accenture from its competitors;
- Professionals and experts: Accenture has many specialists and skilled employees, demonstrating expertise in different sectors.
Accenture Weaknesses
- Poor coordination: When multiple sectors run simultaneously, there can be poor coordination and communication among the team. Despite Accenture’s effort to serve numerous mid-size companies, it faces severe competition, which can slow down growth.
- Consultancy dependence: Consultancy plays a crucial role in Accenture’s revenue generation, which can hurt the firm in the long run;
- Investment in research and development: Accenture has been unable to compete with the core players in the industry regarding research and development and innovation. It paints a picture of a firm that deals with products established on tested attributes in the market;
Accenture Opportunities
- Mergers: A few years ago, Accenture acquired Agilex Technology, an I.T. services, and software provider to the U.S. government, and Brazilian analytical tool company, Gaspo. The company can boost its analytical power through acquisitions that facilitate its expansion;
- New green laws: These possibilities create a level playing field for every industrial participant. Accenture will get a great chance to showcase its dominance in new technologies;
- Low inflation: A low inflation rate provides stability in the market, allowing Accenture’s clients to acquire cheaper loans.
Accenture Threats
- Irregular supply of exclusive items: Accenture has produced different products since its establishment. However, their response is based on availability from other companies. Accenture’s supply of new products is inconsistent, resulting in sales fluctuation over time;
- Competition: The number of companies joining the industry has risen over the years, affecting Accenture’s overall sales and profitability. The demand for profitable products in inconsistent and unpredictable situations during peak seasons can affect a company’s overall profitability.
Conclusion
Even though Accenture has faced stiff competition, it has dominated the market due to its robust network and investments. A solid connection with its clients and skilled workers have played a core role in Accenture’s success.
The company has adopted digital marketing strategies like content marketing, SEO, and email to educate its clients and advertise upcoming and current offers. Accenture combines its unrivaled industry experience, solidity in expertise, global delivery potential, and functional proficiency to deliver substantial results. As the market becomes more competitive every day, Accenture should adopt advanced technologies and processes to remain ahead of competitors.

